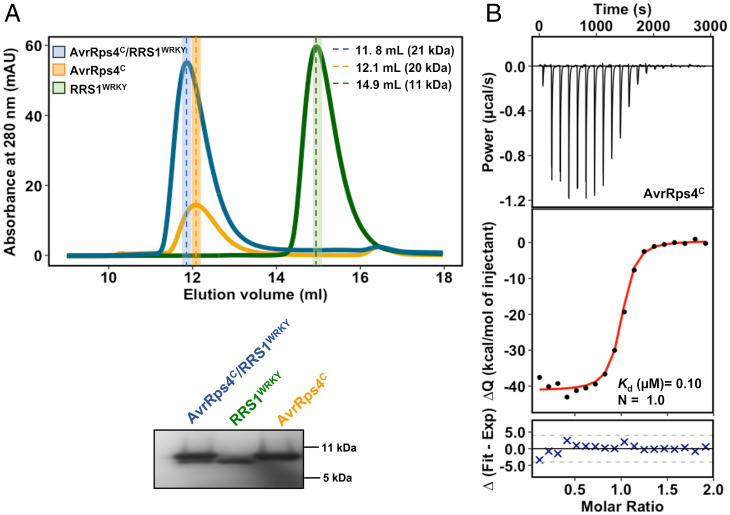
Fig. 1.
AvrRps4C interacts with the WRKY domain of RRS1 in vitro. (A) Analytical gel filtration traces (using a Superdex 75 10/300 column) for AvrRps4C alone (gold), RRS1WRKY alone (green), and AvrRps4C with RRS1WRKY (blue) with sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gels of relevant fractions. An equimolar ratio of AvrRps4C and RRS1WRKY was used for the analysis. AvrRps4C runs as a dimer in vitro. Poor absorbance for AvrRps4C at 280 nm is due to its low molar extinction coefficient. (B) ITC titrations of AvrRps4C with RRS1WRKY. (B, Upper) Raw processed thermogram after baseline correction and noise removal. (B, Lower) The experimental binding isotherm obtained for the interaction of AvrRps4C and RRS1WRKY together with the global fitted curves (displayed in red) were obtained from three independent experiments using AFFINImeter software (61). Kd and binding stoichiometry (N) were derived from fitting to a 1:1 binding model.