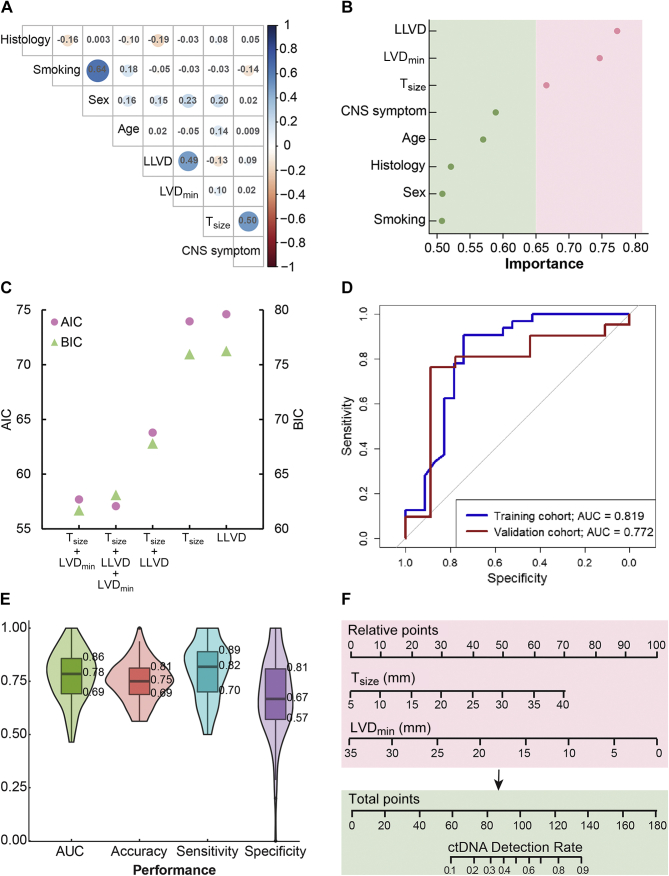
Figure 3.
Feature selection and validation of the logistic regression model.
(A) The correlation of all clinical features. Blue shade represents a positive correlation and red shade represents a negative correlation. The correlation values of any two features are labeled in the intersectant squares with color-scaled circles. (B) Results of the variate importance analysis of all clinical features. (C) Model selection based on the AIC and BIC methods. (D) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for the training cohort (n = 66) and validation cohort (n = 30). (E) Internal cross-validation in the training cohort based on two variables, Tsize and LVDmin. A random split (7 : 3) sample approach was repeated 100 times. (F) The nomogram was built to estimate the probability of detecting CSF ctDNA in the training cohort. A probability of more than 0.5 is considered beneficial for patients if they are subject to CSF liquid biopsies.
AIC, Akaike information criterion; AUC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; BIC, Bayesian information criterion; CNS, central nervous system; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; LLVD, shortest lesion–ventricle distance for the largest lesion; LVDmin, minimum lesion–ventricle distance for all intracranial lesions; Tsize, the maximum diameter of the largest intracranial lesion.