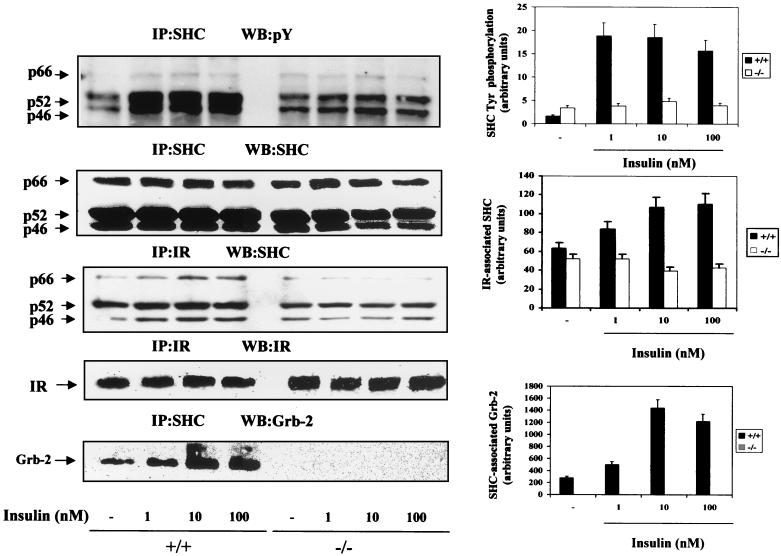
FIG. 3.
Insulin effect on SHC tyrosine phosphorylation and its association with an insulin receptor and Grb-2 in wild-type and IRS-1-deficient brown adipocytes. Quiescent (20-h serum-starved) wild-type (+/+) and IRS-1-deficient (−/−) brown adipocytes were stimulated with insulin (1 to 100 nM) for 5 min. Control cells were cultured in the absence of the hormone. At the end of the culture time, cells were lysed and 600 μg of total protein was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-SHC or anti-insulin receptor (IR) antibodies. The resulting immune complexes were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with anti-Tyr(P), anti-SHC, anti-IR, and anti-Grb-2 antibodies as indicated in each panel. The positions of p66, p52, and p46 SHC proteins and IR β-chain and Grb-2 are indicated by arrows. The results shown are representative of three experiments, which used two clones of each cell type. The corresponding autoradiograms were quantitated by scanning densitometry. Results are expressed as arbitrary units of SHC tyrosine phosphorylation, IR-associated SHC, or SHC-associated Grb-2 and are means ± standard errors.