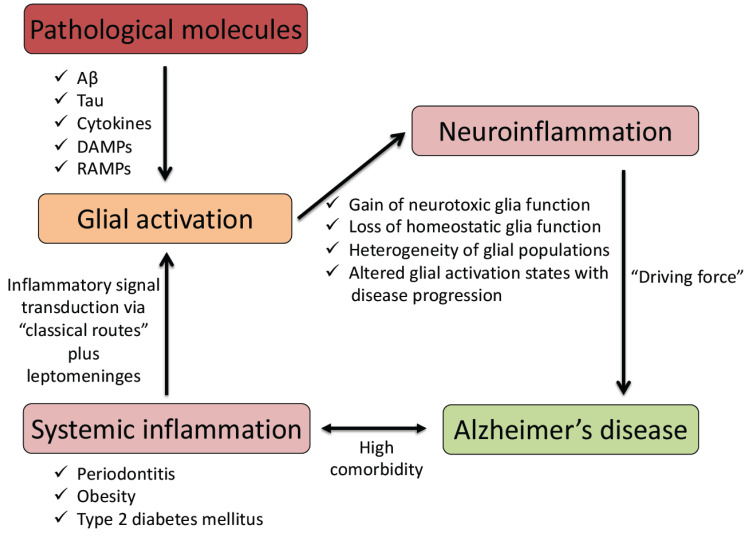
Fig. (1).
A schematic diagram showing links between systemic inflammation, glial activation, and neuroinflammation contributing to the pathogenetic mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Aβ, amyloid-β peptides; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; RAMPs, resolution-associated molecular patterns. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).