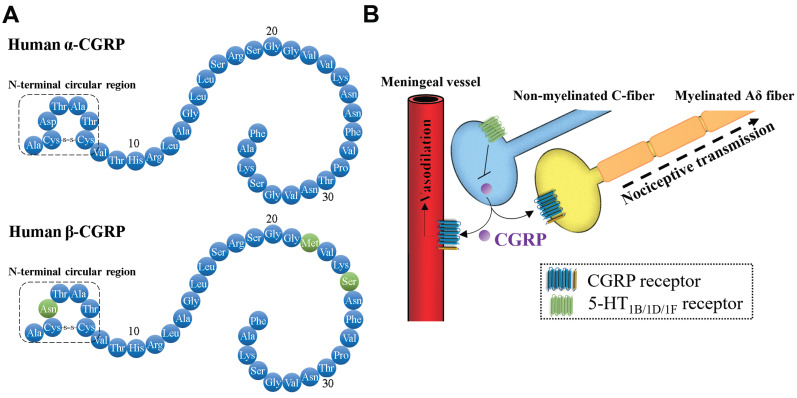
Fig. (1).
The roles of CGRP in trigeminovascular system. (A) Mature peptide of human α-CGRP and β-CGRP. (B) In the trigeminovascular system, the released CGRP from non-myelinated C-fiber can bind to the CGRP receptor in vascular endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells, subsequently promote the production of NO to trigger vasodilation. In addition, CGRP bind to the CGRP receptor in the terminal of nociceptive transmission from trigeminal nerves to the sensory cortex. Activation of 5-HT1B/1D/1F receptors signaling can block the release of CGRP from C-fiber. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).