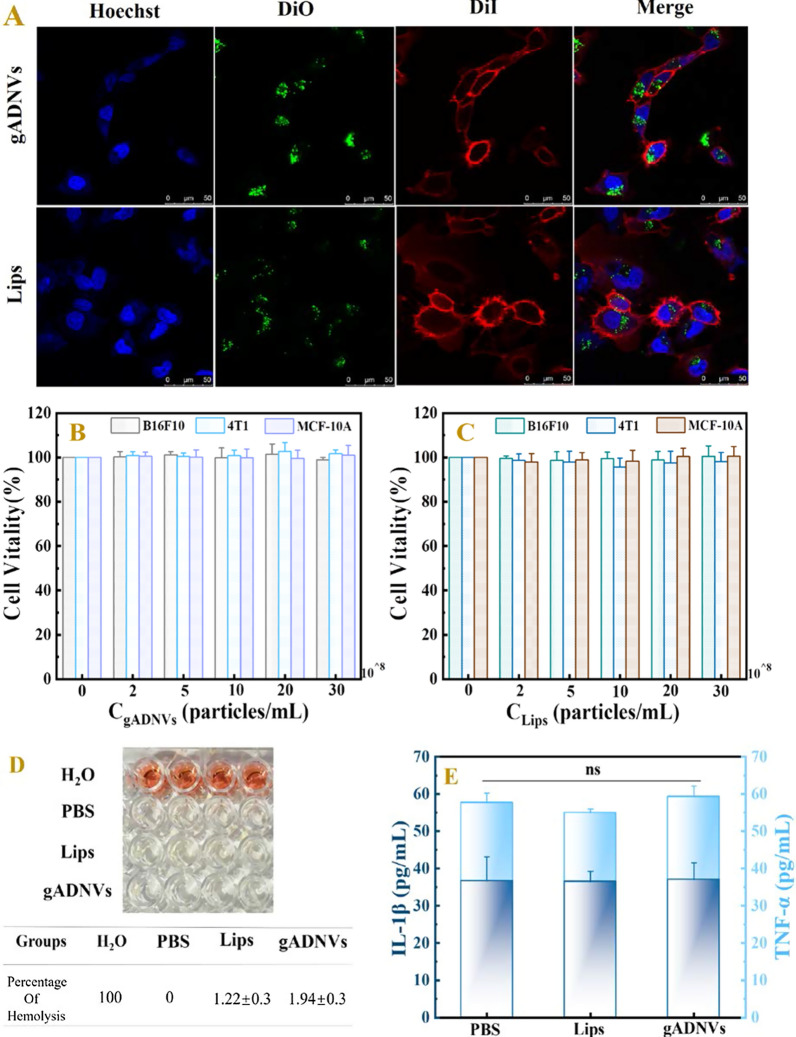
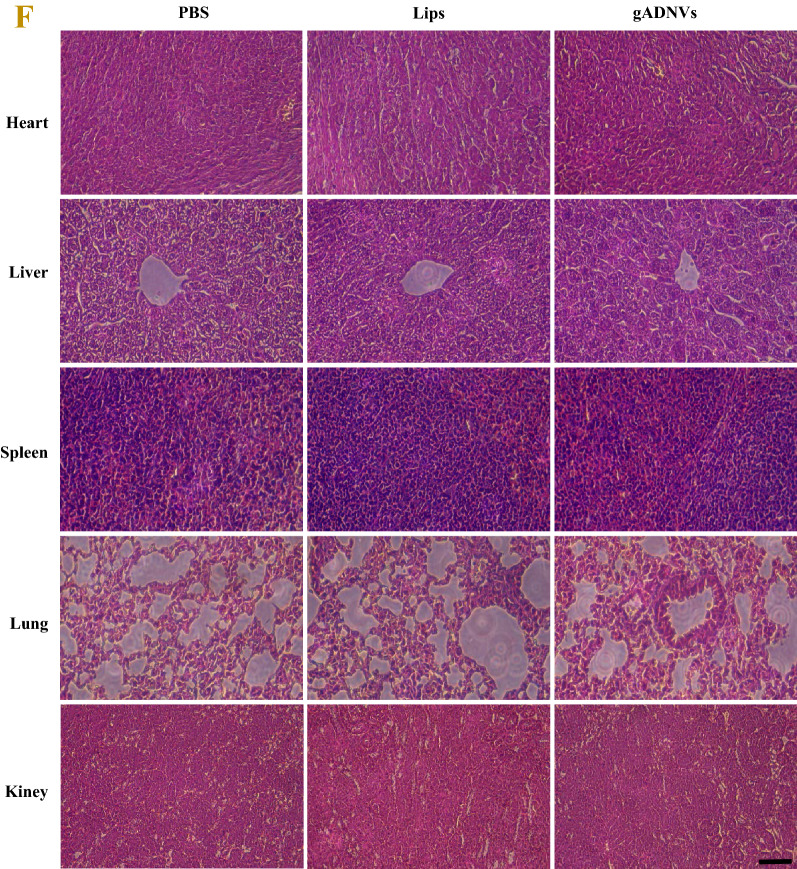
Fig. 4.
The safety assessment of gADNVs in vitro and in vivo. A The cellular uptake of gADNVs analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscope. DAPI (blue) was the nuclear staining channel; DiO (green) was the channel of gADNVs and Lips; DiI (red) was the cell membrane staining channel. B The vitality of B16F10, 4T1 and MCF-10A cells analyses by MTT assay after treating with different concentrations of gADNVs. C The viability of B16F10, 4T1 and MCF-10A cells analyzed by MTT assay after treating with different concentrations of Lips. D The hemolysis assay of gADNVs and Lips. The group treated with ultrapure water was set as a positive control with the hemoglobin release rate of 100%, and the group treated with PBS was used as a negative control. E The changes of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β) in mice after PBS, gADNVs and Lips injection. F H&E staining of heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney sections treated with PBS, gADNVs and Lips. Scale bar was 100 μm. Data in B, C and E represent mean values ± SD, n = 3. Statistical differences were analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t-test, ns shows that there is no significant difference between the compared data