FIGURE 1.
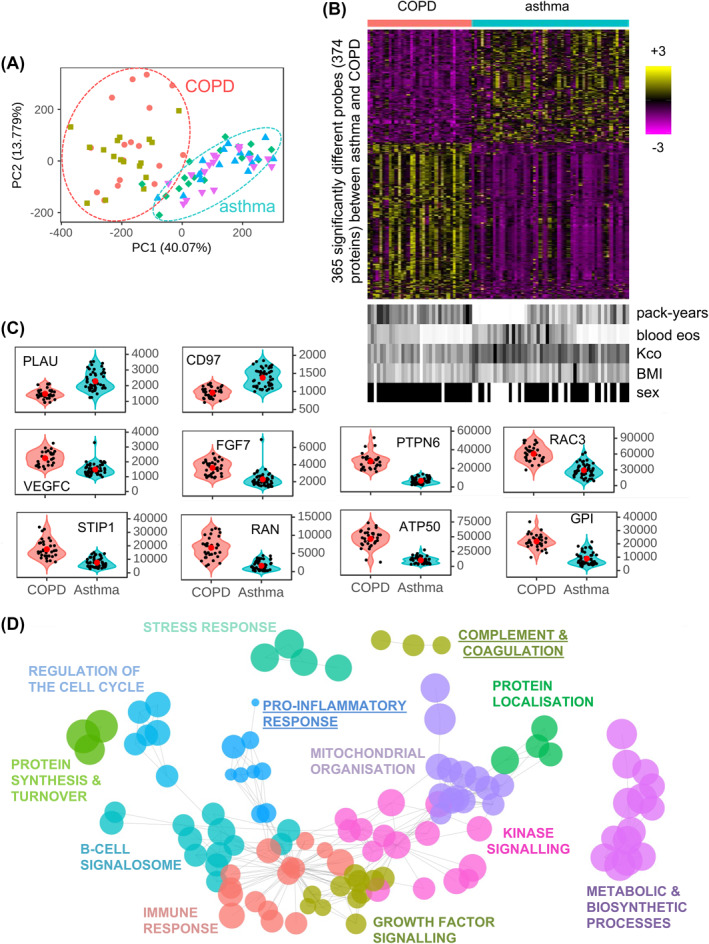
The plasma proteome differs between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. The plasma proteome was compared between all COPD and all asthma subjects. (A) A principal component analysis (PCA) scatterplot across all COPD and asthma subjects showing PC1 versus PC2. In the PCA scatterplots, the percent variation explained by each component is given on the axis label. COPD subjects with ( ) or without (
) or without ( ) low blood eosinophils and bronchodilator reversibility. Asthma subjects with a smoking history and with high (
) low blood eosinophils and bronchodilator reversibility. Asthma subjects with a smoking history and with high ( ) or low (
) or low ( ) blood eosinophils, and asthma with no smoking history and high blood eosinophils (
) blood eosinophils, and asthma with no smoking history and high blood eosinophils ( ). (B, upper) Heatmap of abundances for 365 significantly (p ≤ 0.05) different SOMAscan® probes between COPD (red bar) and asthma (blue bar) subjects. The color intensity represents row scaled (z‐score) protein abundance, with magenta as low and yellow as high abundance. The heatmap has been hierarchically clustered by row. (B, lower) For each subject, selected clinical features are given in a paired heatmap showing: smoking index (pack‐years), blood eosinophil counts (bld eos), Kco, % predicted (Kco), body mass index (BMI), and sex. Values for each feature are represented as a grayscale, with white as low and black as high except sex where females are white, and males are black. (C) Violin plots of protein abundances for selected proteins of COPD (red) and asthma (blue) subjects. Individual subjects are shown as black dots, and disease means as larger red dots. Protein abundance is given on the y‐axis. (D) Results from protein‐set enrichment analysis for COPD versus asthma. The results are summarized as a network, where each enriched protein‐set (p ≤ 0.001) is given as a node (circles) and protein‐sets with >50% of genes in common are connected by edges (lines). Representative names and arbitrary colors are given for each cluster. Node size represents the size of the difference between COPD and asthma by observed/random earth mover's distance score. Those pathways underlined are elevated in asthma as compared to COPD
). (B, upper) Heatmap of abundances for 365 significantly (p ≤ 0.05) different SOMAscan® probes between COPD (red bar) and asthma (blue bar) subjects. The color intensity represents row scaled (z‐score) protein abundance, with magenta as low and yellow as high abundance. The heatmap has been hierarchically clustered by row. (B, lower) For each subject, selected clinical features are given in a paired heatmap showing: smoking index (pack‐years), blood eosinophil counts (bld eos), Kco, % predicted (Kco), body mass index (BMI), and sex. Values for each feature are represented as a grayscale, with white as low and black as high except sex where females are white, and males are black. (C) Violin plots of protein abundances for selected proteins of COPD (red) and asthma (blue) subjects. Individual subjects are shown as black dots, and disease means as larger red dots. Protein abundance is given on the y‐axis. (D) Results from protein‐set enrichment analysis for COPD versus asthma. The results are summarized as a network, where each enriched protein‐set (p ≤ 0.001) is given as a node (circles) and protein‐sets with >50% of genes in common are connected by edges (lines). Representative names and arbitrary colors are given for each cluster. Node size represents the size of the difference between COPD and asthma by observed/random earth mover's distance score. Those pathways underlined are elevated in asthma as compared to COPD
