Fig. 5. SasA and KaiB bind to the same site on KaiC.
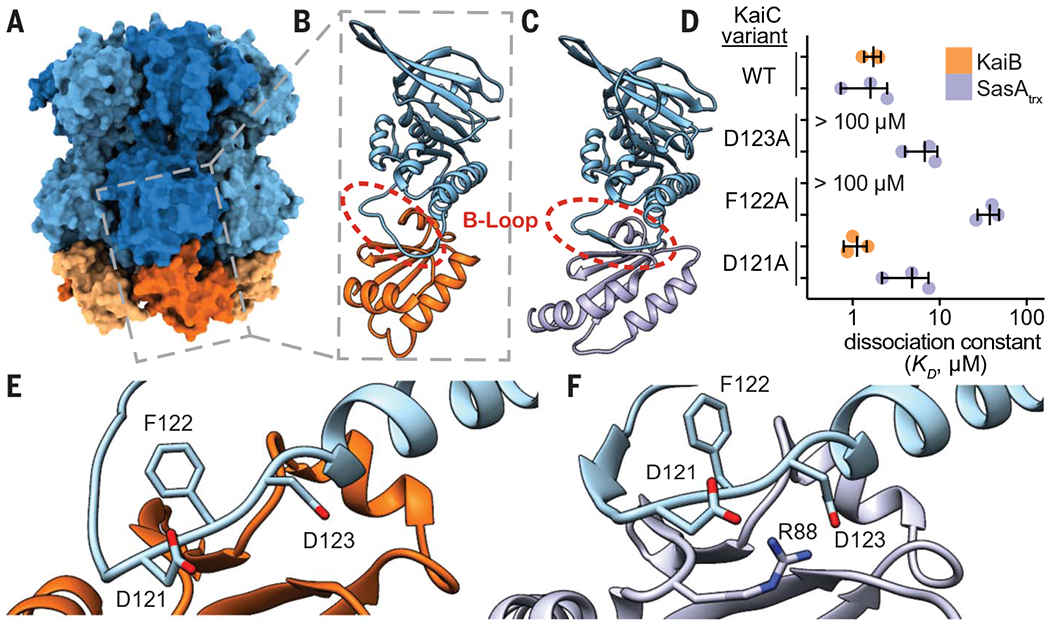
(A) The KaiB-KaiC heterododecamer [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID 5JWQ] with subunits of the KaiC ring depicted in alternating light and dark blue, and fsKaiB subunits in alternating light and dark orange. The gray box indicates the position of (B) the isolated KaiC-CI domain-fsKaiB subcomplex (PDB ID 5JWO). (C) The KaiC-CI domain–SasAtrx subcomplex (PDB ID 6X61), with KaiC (blue) and SasA (purple). (D) Equilibrium dissociation constants (KD) for KaiB (orange) or SasAtrx (purple) binding to KaiC-EE mutants (mean ± SD, n = 3). Where indicated, binding was too weak for curve fitting, and KD is reported as >100 μM. Single-letter abbreviations for the amino acid residues are as follows: A, Ala; C, Cys; D, Asp; E, Glu; F, Phe; G, Gly; H, His; I, Ile; K, Lys; L, Leu; M, Met; N, Asn; P, Pro; Q, Gln; R, Arg; S, Ser; T, Thr; V, Val; W, Trp; and Y, Tyr. (E and F) The interface of KaiC-CI with fsKaiB (E) or SasAtrx (F) with key residues highlighted.
