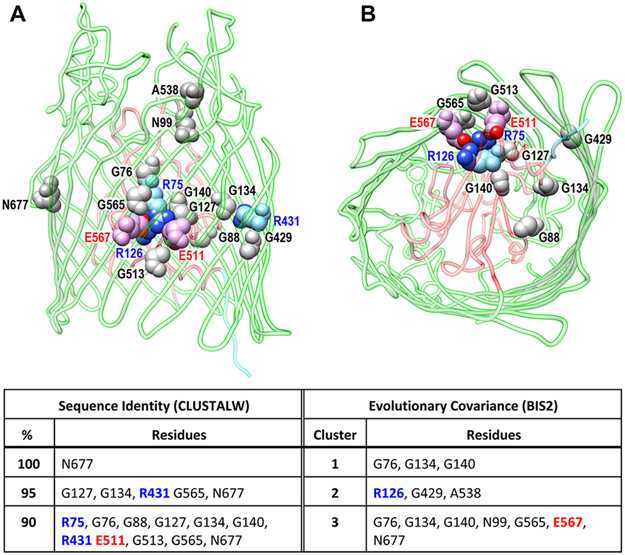
Figure 5.
Conserved mechanistic charge cluster in the LGP interior. After aligning the primary structures of 79 LGP from commensal and pathogenic Gram (−) bacteria (Table 1) by CLUSTALΩ664 and analyzing the aligned files for evolutionary covariance by BIS2,665 we mapped 16 conserved (>90%) or coevolved amino acids to the tertiary structure of EcoFepA (PDB 1FEP) using CHIMERA (UCSF716). (A) Side view of EcoFepA: the N-domain (residues 1–150) is depicted in ribbon format and colored red; the C-domain β-barrel (residues 151–7240 is depicted in ribbon format and colored green. Among the 16 residues of interest (shown in space-filling fomat), one (N677, colored gray) was conserved in all the LGP. (B) −90° X-axis rotation of the view in (A) creates a perspective inside the β-barrel, from the periplasm. Four polar charged side chains (R75, R126, E511, E567; colored sky blue and red, respectively; heteroatoms N and O colored blue and red, respectively) create an electrostatic lock that, in the absence of protonation, holds the N-domain to the β-barrel directly above the TonB-box region (in ribbon format, colored cyan). A group of eight glycines (colored gray), located in either the interior of the N-domain (G76, G88, G127, G134, G140) or in the strands of the β-barrel (G429, G513, G565), surround the charge cluster, potentially maximizing the flexibility of the protein structure in this region.