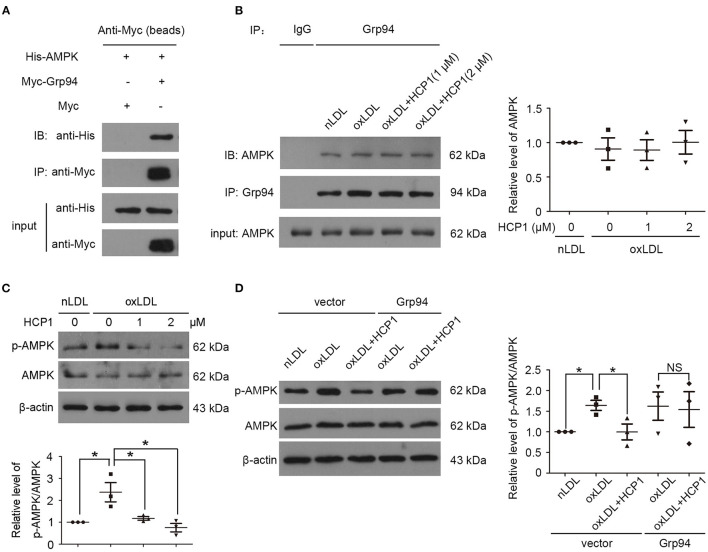
Figure 3.
Grp94 might interact with AMPK and activate its activity. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of His-tagged AMPK proteins with Myc-tagged Grp94 from HEK293T cells transfected His-AMPK with Myc (lane 1) or Myc-Grp94 (lane 2). The lower panel showed expression levels of His-AMPK and Myc-Grp94 in the experiment. (B) Co-IP of AMPK with Grp94 from HUVECs treated with nLDL (50 μg/ml), oxLDL (50 μg/ml) with or without HCP1 (1, 2 μM) for 3 h. Co-immunoprecipitated AMPK was quantified in immunoblot with anti-AMPK antibody in western blot. (C) Protein levels of phosphorylated AMPKα (p-AMPKα, Thr172) and total AMPKα in HUVECs treated with nLDL (50 μg/ml), oxLDL (50 μg/ml) with or without HCP1 (1, 2 μM) for 6 h. Bar charts show quantification of the ratio of p-AMPKα to total AMPKα. (D) Protein levels of phosphorylated AMPKα (p-AMPKα, Thr172) and total AMPKα in HUVECs transfected with c-Myc empty vector or c-Myc-Grp94-wt plasmid for 24 h were detected after treatment with nLDL (50 μg/ml), oxLDL (50 μg/ml) with or without HCP1 (1 μM) for 6 h. Data are mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, NS p > 0.05; n = 3. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA.