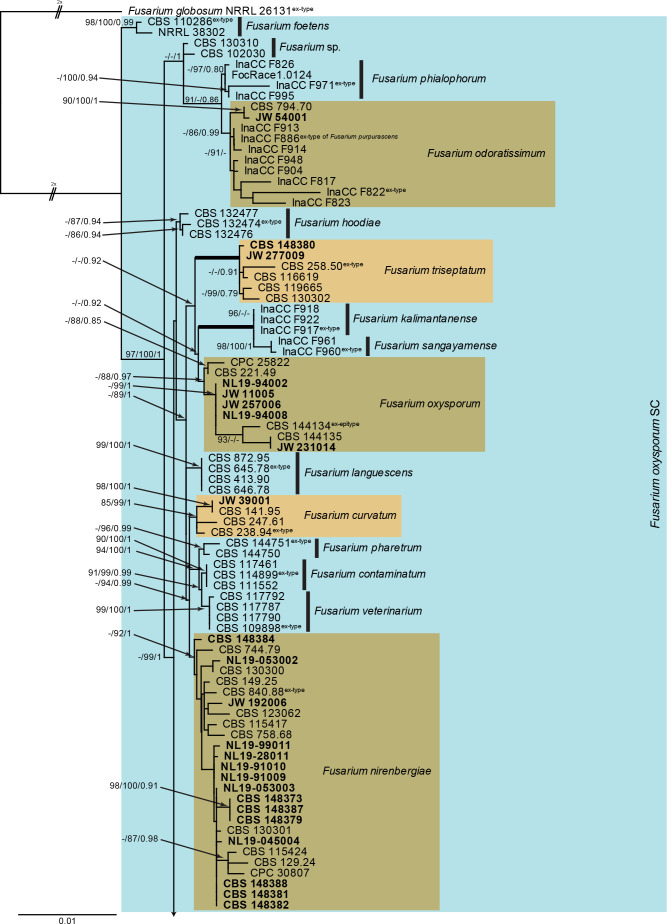
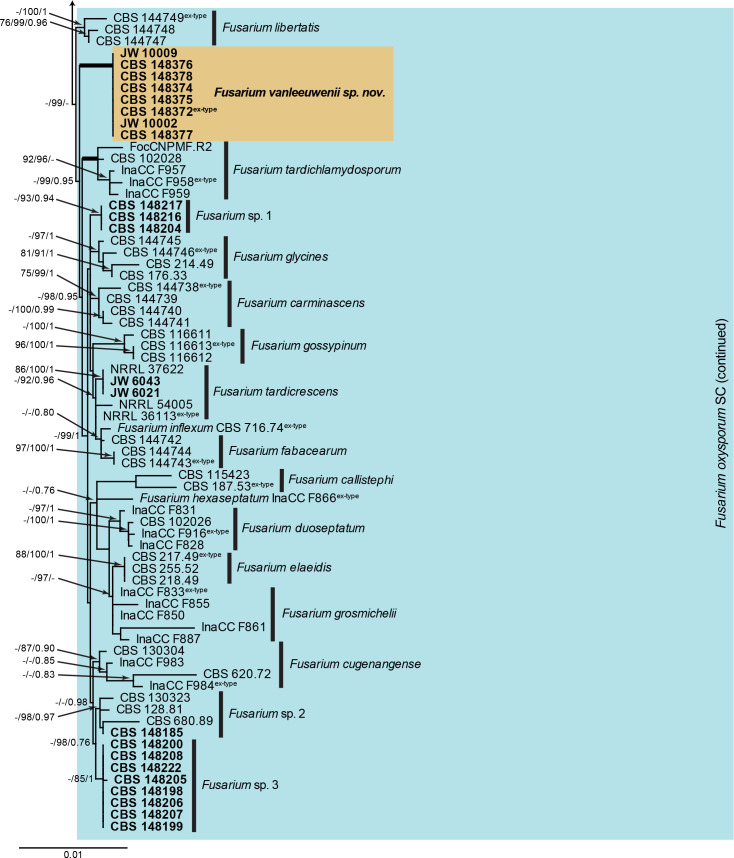
Fig. 3.
The RAxML consensus tree inferred from the combined F. oxysporum species complex tef1, rpb2 (first part), tub2, cmdA and rpb1 sequence alignment. Thickened lines indicate branches with full support (RAxML & IQ-TREE bootstrap = 100 %; PP = 1.0) with support values of other branches indicated at the branches (RAxML > 74 % / IQ-TREE > 84 % / PP > 0.74). The tree is rooted to Fusarium globosum (NRRL 26131) and the two basal branches were halved to facilitate layout. The scale bar indicates the number of expected changes per site. The F. oxysporum species complex is indicated on the right and highlighted with a coloured block. Species clades containing the novel citizen science strains (in bold) are highlighted with coloured blocks and the novelty described in the present study is printed in bold font.