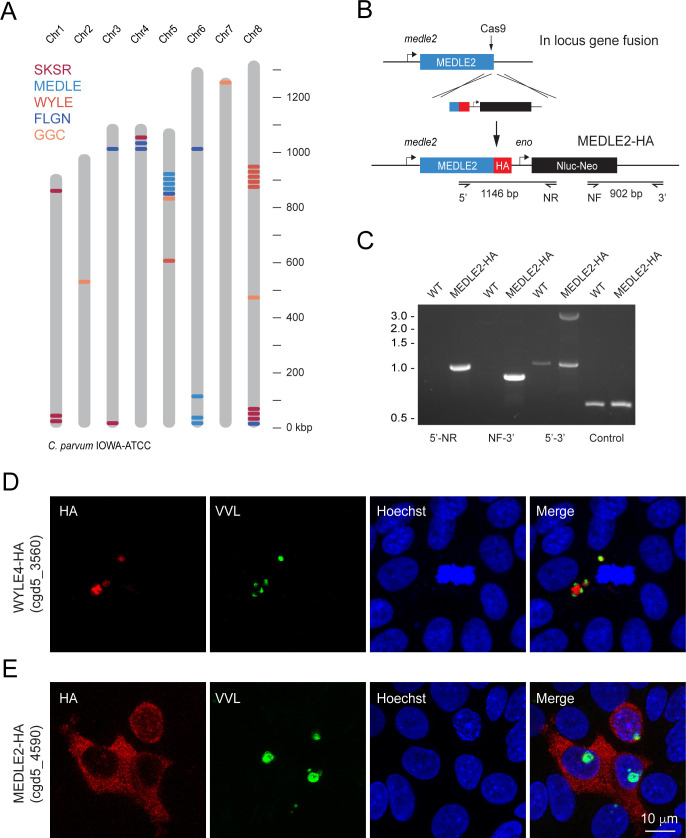
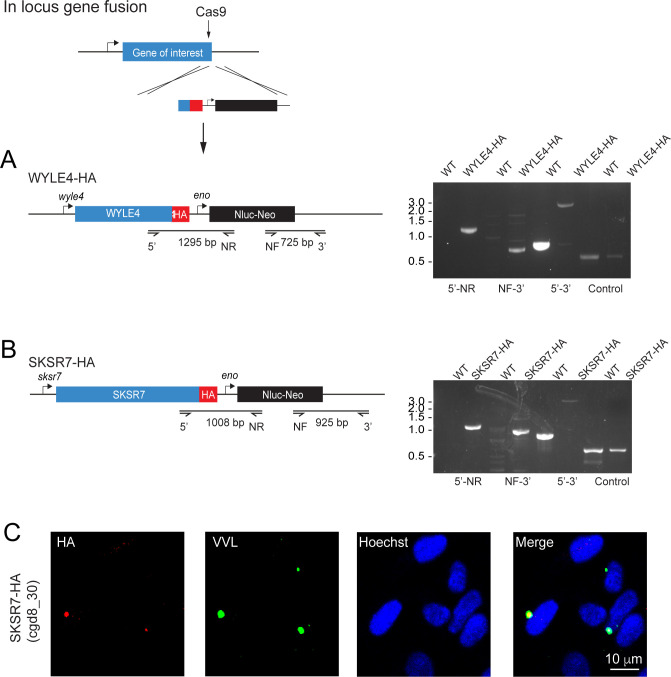
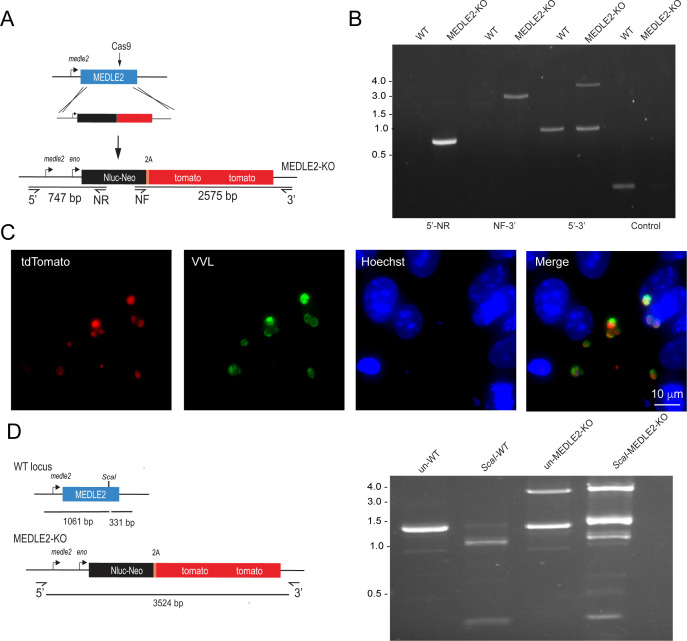
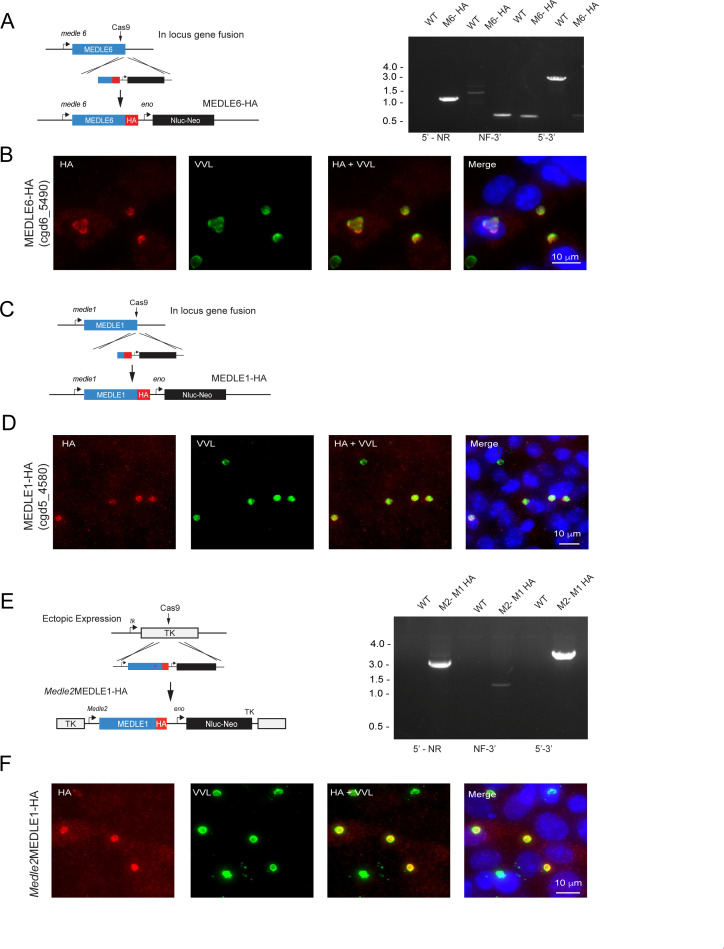
Figure 1. MEDLE2 is exported to the host cell cytoplasm.
(A) Schematic overview of the chromosomal location for polymorphic gene families in the C. parvum genome. (B) Map of the MEDLE2 locus targeted in C. parvum for insertion of a 3× hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tag, a nanoluciferase reporter gene (Nluc), and neomycin phosphotransferase selection marker (Neo). (C) PCR mapping of the MEDLE2 locus using genomic DNA from wild type (WT) and transgenic (MEDLE2-HA) sporozoites, corresponding primer pairs are shown in (B), and thymidine kinase (TK) gene used as a control. Note the presence of two bands in the 5′–3′ amplification, indicating the presence of a transgene (3081 bp) and persistence of an unmodified copy (1174 bp), suggesting multiple copies of MEDLE2 in the C. parvum genome; also see Figure 1—figure supplement 2. (D, E) HCT-8 cultures were infected with WYLE4-HA (D) or MEDLE2-HA (E) transgenic parasites and fixed after 24 hr for immunofluorescence assay (IFA). Red, antibody to HA; green, Vicia villosa lectin stain, VVL (Gut and Nelson, 1999); blue, Hoechst DNA dye. Additional genes targeted and the localizations of their products are summarized in Table 1 and Figure 1—figure supplements 1 and 3.