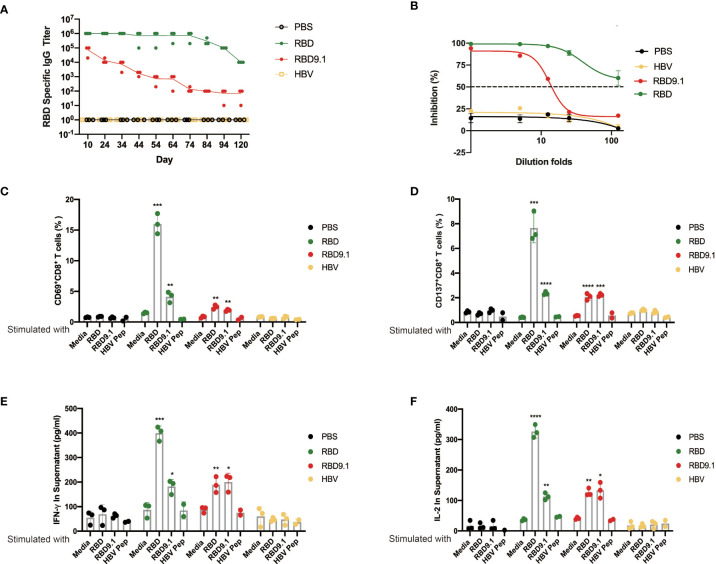
Figure 6.
(A) RBD9.1 antigenic peptide induced long-term protection. Receptor-binding domain (RBD)–binding immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody ELISA titers by mouse sera taken 10, 24, 34, 44, 54, 64, 74, 84, 94, and 120 days following the last immunization. (B) RBD-blocking assay for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (wild-type) by mouse sera taken 64 days following the last dose of RBD or RBD9.1. (C) The expressions of CD69 and CD137 (D) (gated on CD8+ T cells of immune mice) were detected by flow cytometry after 10 μg/ml RBD, RBD9.1, or HBV peptide stimulation for 24 h; normal medium was used as negative control. (E) The quantities of interleukin (IL)-2 and interferon (IFN)-γ (F) in the supernatant were detected by ELISA after 10 μg/ml of RBD, RBD9.1, or HBV peptide stimulation for 48 h; normal medium or HBV peptide was used as corresponding negative control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.