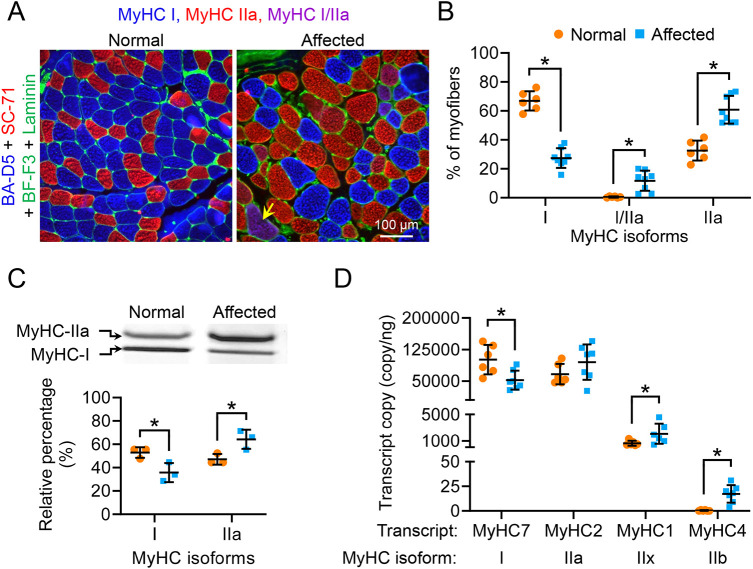
Fig. 7.
Affected dog ECU muscle displayed a slow-to-fast myofiber-type switch. (A) Representative MyHC immunostaining photomicrographs of the ECU muscle from a normal and an affected ECU muscle. Blue, type I myofiber; red, type IIa myofiber; magenta (yellow arrow), type I/IIa hybrid myofiber; green, laminin immunostaining. (B) Quantification of fiber-type composition in normal (n=6) and dystrophic (n=8) ECU muscle by immunofluorescence staining. (C) Electrophoresis separation and quantification of ECU muscle fiber type. Upper panel, representative electrophoresis silver staining image of the MyHC isoforms in normal and dystrophic ECU muscle. Lower panel, quantification of the relative percentage of type I and type IIa isoforms in normal (n=3) and dystrophic (n=3) ECU muscle. (D) Quantification of skeletal muscle MyHC isoform transcripts in normal (n=6) and dystrophic (n=7) ECU muscle. Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.05 (statistical analysis was performed using multiple unpaired t-tests in B-D).