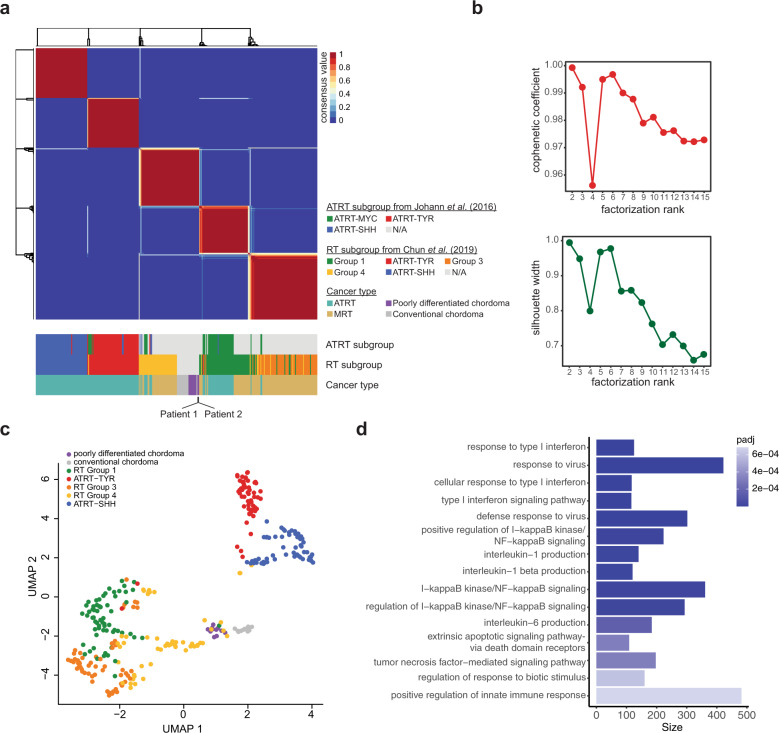
Fig. 5. Methylation clustering reveals common immune response pathway activities with a subset of extra-cranial malignant rhabdoid tumours.
a DNA methylation clustering using non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) of paediatric chordoma data from this study (n = 2) and Hasselblatt et al.2 (n = 23), atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumours (ATRT, n = 161) and extra-cranial rhabdoid tumours (MRT, n = 131). The respective ATRT subgroups identified in Johann et al.74 and rhabdoid tumour (RT) subgroups identified in Chun et al17. are displayed in the track below. b Cophenetic coefficients (top) and silhouette widths (bottom) for NMF cluster solutions from k = 2 to k = 15. A robust clustering result was obtained at k = 5, with high cophenetic coefficient and silhouette width. c Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) clustering of RTs with chordomas. d Gene set enrichment analysis of genes with differentially methylated CpGs in paediatric chordoma compared to RT subgroups 1–3 and 5 using a logistic regression model corrected for the number of CpGs in the gene set using methylGSA73. The number of genes associated with the gene ontology (GO) terms are shown and bars are coloured by FDR adjusted p values. The most significantly enriched terms, i.e. type I interferon, response to virus and type I interferon signalling pathway, had adjusted p values of 2.93e−08, 7.55e−08 and 1.13e−07, respectively.