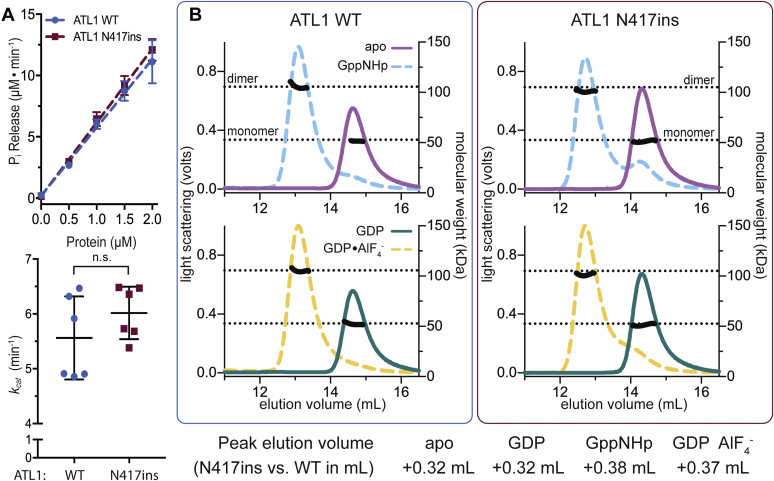
Figure 3.
GTP hydrolysis and nucleotide-dependent dimerization of ATL1 N417ins.A, GTP hydrolysis measured via release kinetics of Pi for ATL1 WT and N417ins catalytic cores across protein concentrations (0–2 μM) are shown (top panel). Symbols represent the mean of two biological and three technical replicates with error bars showing standard deviations (SD). Apparent turnover rates (kcat) were calculated from the Pi-release kinetics for each replicate with the middle bar representing the mean and error bars showing SD. An unpaired t test evaluated significance (p = 0.0858). B, nucleotide-dependent oligomerization. Chromatograms from SEC-MALS experiments with either ATL1 WT (left) or N417ins (right), with all colored lines representing light scattering signal in volts denoted on the left axis (GppNHp, apo, GDP•AlF4−, and GDP), and black lines indicating calculated molecular weight in kDa (right axis). Dotted lines represent the theoretical molecular weights of the monomer and dimer (52.9 kDa and 105.8 kDa for N417ins; 52.8 kDa and 105.6 kDa for WT). For each nucleotide condition, the volume at the maximum light scattering signal for WT was subtracted from that of N417ins and the shift is indicated in ml (bottom text).