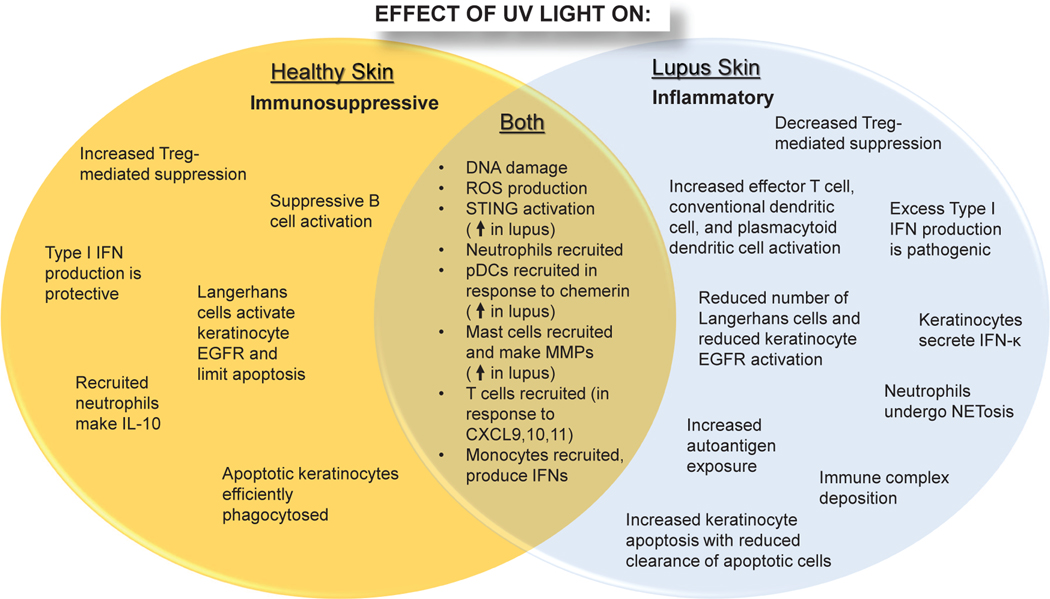
Figure 1: Overview of differential effects of UV light on healthy vs. lupus skin.
In healthy skin (left), UV light generates an immunosuppressive environment characterized by efficient clearance of apoptotic cells, immune cell activation, and secretion of protective/suppressive cytokines including type I interferons (IFNs) and IL-10. In lupus skin, UV light exposure is inflammatory secondary to increased immune cell infiltration, inhibition of negative regulatory mechanisms, and amplified production of type I IFNs that enhance keratinocyte apoptosis. Apoptotic cells are not efficiently cleared resulting in increased autoantigen exposure, immune complex formation, and lesion development.