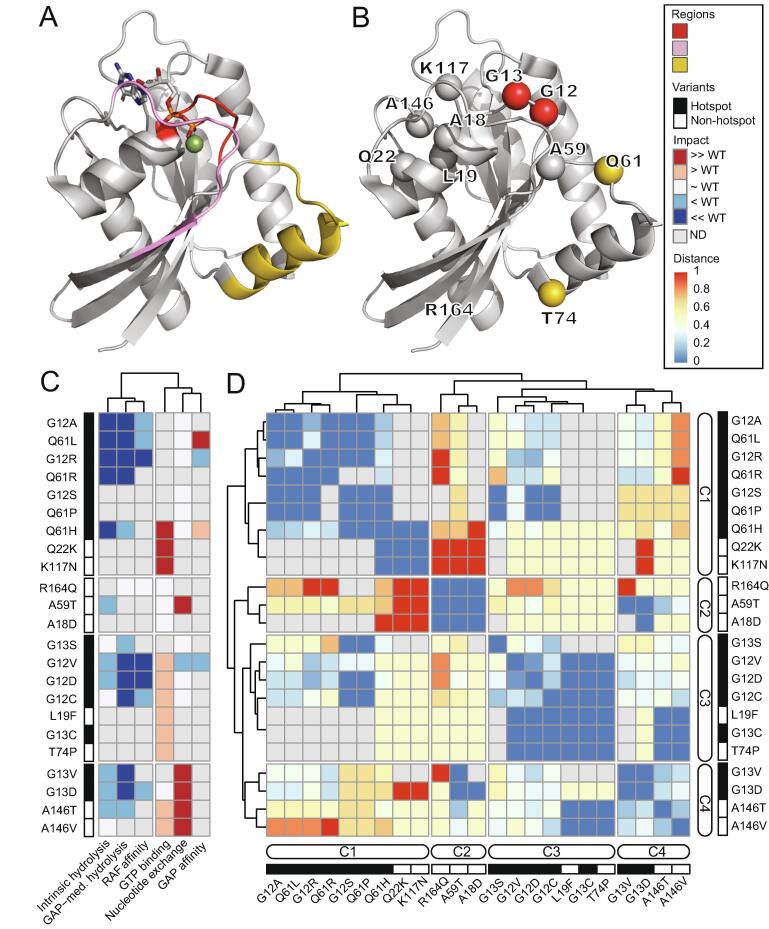
Fig. 1.
Semi-quantified biochemical measurements elucidate the similarities and differences among the hotspot and non-hotspot variants. A) 3D structure of KRAS (PDB: 4OBE) representing the sensitive regions, phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) (amino-acid 10–17), switch-I (amino acids 30–40) and switch-II (amino acids 60–76) [38]. B) 23 KRAS hot-spot and non-hotspot variants that belong to 11 amino-acid residues are projected onto the 3D structure. The amino-acid residues are colored according to the sensitive regions in (A). C) Heatmap of the semi-quantified 6 experimental measurements (representing the columns) of the 23 KRAS variants demonstrates the variable biochemical properties of mutant KRAS proteins relative to WT, and by ordering the variants (representing the rows) according to the four clusters in panel D. The complete summary data with references is in Table S1. D) The dissimilarity among the 23 KRAS variants based on the experimental assay in panel C using Gower distance. The variants with distance 0 are identical and shown in blue, whereas the maximally dissimilar variants with distance 1 are shown in red color. The dendrograms show for distinct clusters are indicated as C1, C2, C3 and C4. The hotspot and non-hotspot KRAS variants are indicated by black and white rectangles, respectively. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)