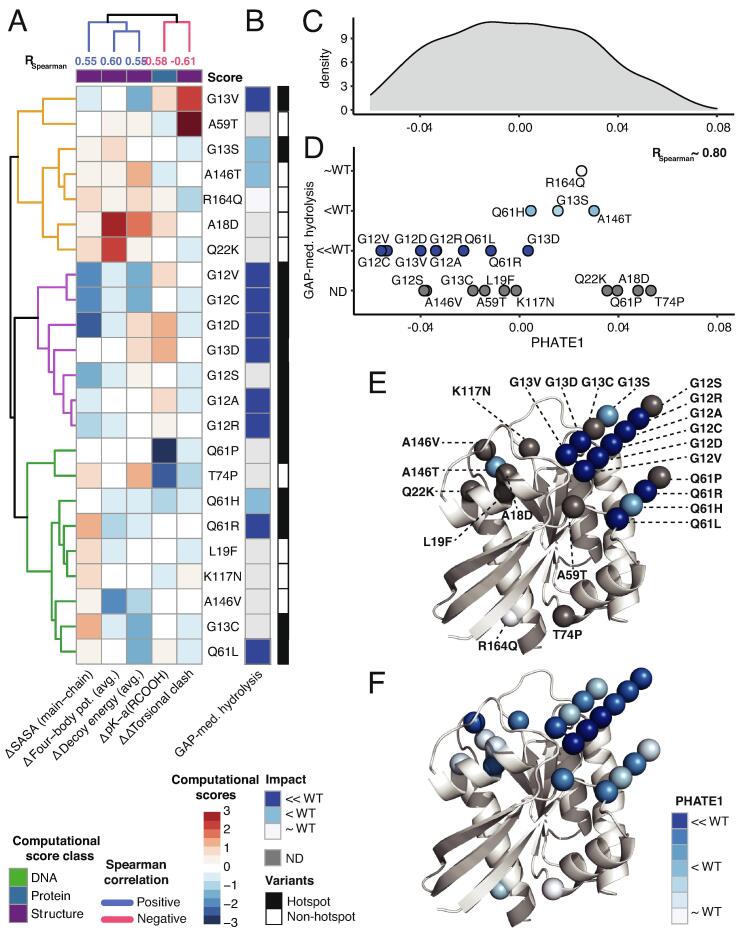
Fig. 3.
3D structure and protein sequence-based scores unravel the mechanism of disruption of GAP-mediated hydrolysis. A) Five computational scores (4 3D structure and 1 protein sequence -based) for the 23 KRAS variants that strongly correlate with the GAP-mediated hydrolysis measurements. The computational scores from protein sequence (blue) and 3D structure (purple) are represented as z-scores from high (red) and low (blue), with upper dendrogram colored by correlation with GAP-mediated hydrolysis measurements. B) Semi-quantified measurements of the GAP-mediated hydrolysis of the KRAS variants based on the similarity to the WT. Next, we performed 1D PHATE analysis of the 935 variants from 7 RAS genes using the 5 correlated computational scores from (A) for mechanistic interpretation of GAP-mediated hydrolysis. C) 1D probability density plot of PHATE1 for all the 935 RAS variants. D) Scattered plot of the 23 KRAS variants (out of 935) along the PHATE1 coordinate that show RSpearman ∼ 0.80 with the GAP-mediated hydrolysis measurements. The variants are colored and separated vertically based on their GAP-mediated hydrolysis value. E) The 23 KRAS variants are projected onto the 3D structure and colored according to experimentally measured GAP-mediated hydrolysis values, or F) PHATE1 values from panel D. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)