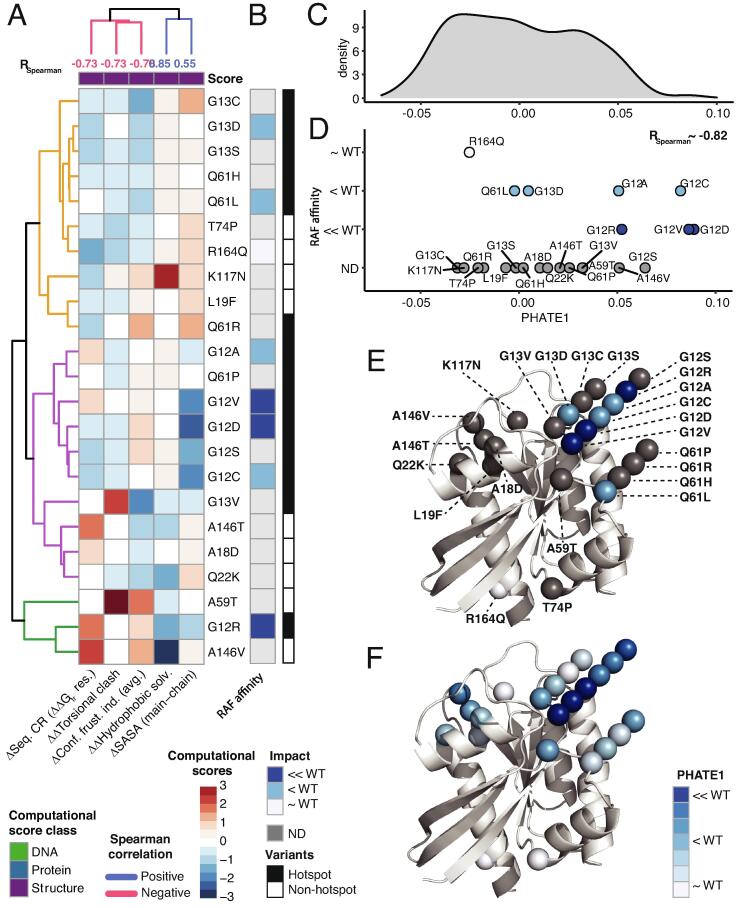
Fig. 4.
Structure-based scores reveal differential mechanism of dysfunction of RAF affinity among the hotspot and non-hotspot variants. A) Pattern of the five 3D structure-based computational scores (as z-scores) for the 23 KRAS variants that B) strongly correlate with semi-quantified RAF affinity measurements (visualizations as in Fig. 3). C) Next, we performed 1D PHATE analysis of the 935 variants from 7 RAS genes using the 5 computational scores for RAF affinity, and summarize using probability density across all the 935 variants. D) Scatter plot of the 23 variants (out of 935 variants) along the PHATE1 coordinate that show RSpearman ∼ 0.85 with the RAF affinity measurements. The 23 variants are colored and separated vertically based on RAF affinity, and classic hotspot mutations are on the upper tail of the distribution. The 23 KRAS variants are projected onto the 3D structure and colored according to E) RAF affinity and F) PHATE1 values.