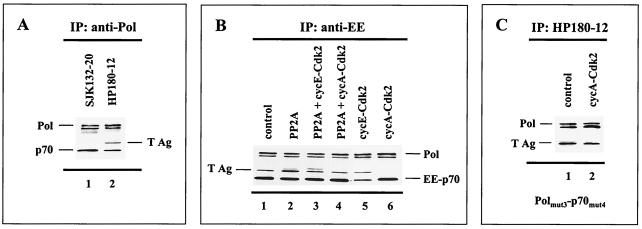
FIG. 6.
Cyclin A-Cdk-dependent phosphorylation of Pol-Prim abrogates complex formation with SV40 T Ag. Human Pol-Prim and T Ag were baculovirus coexpressed with modifying recombinant enzymes as indicated. One hundred to 200 μg of protein extract was used for the coimmunoprecipitation (IP) assays. The precipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide) followed by Western blot analysis. (A) Pol-Prim complexes that were coexpressed with T Ag were precipitated by anti-p180 monoclonal antibodies SJK132-20 (lane 1) and HP180-12 (lane 2). The p180 (Pol) and p70 (p70) subunits of precipitated Pol-Prim plus coimmunoprecipitating T Ag were detected with monoclonal antibodies anti-p180 HP180-7 (1:5), anti-p70 (1:5, 000), and anti-T Ag Pab101 (1:10). (B) Complex formation of recombinant Pol-Prim with T Ag in the absence (lane 1) or presence of coexpressed PP2A (lane 2), PP2A/cyclin E-Cdk2 (lane 3), PP2A/cyclin A-Cdk2 (lane 4), cyclin E-Cdk2 (lane 5), and cyclin A-Cdk2 (lane 6) was investigated by immunoprecipitation with the monoclonal antibody anti-EE for the EE-tagged p70 subunit. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed with monoclonal antibodies anti-p180 HP180-7 (1:5) and anti-EE (1:10). The presence of coimmunoprecipitating T Ag was detected as described above. (C) Complex formation of the Pol α(3xA) and p70(4xA) phosphorylation mutants with T Ag in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of cyclin A-Cdk2 was investigated with the monoclonal p180 antibody HP180-12, which is specific for its hypophosphorylated antigen. The presence of mutant Pol α and coimmunoprecipitating T Ag was detected with monoclonal antibodies anti-p180 HP180-7 (1:5) and anti-T Ag Pab101 (1:10).