Fig. 3.
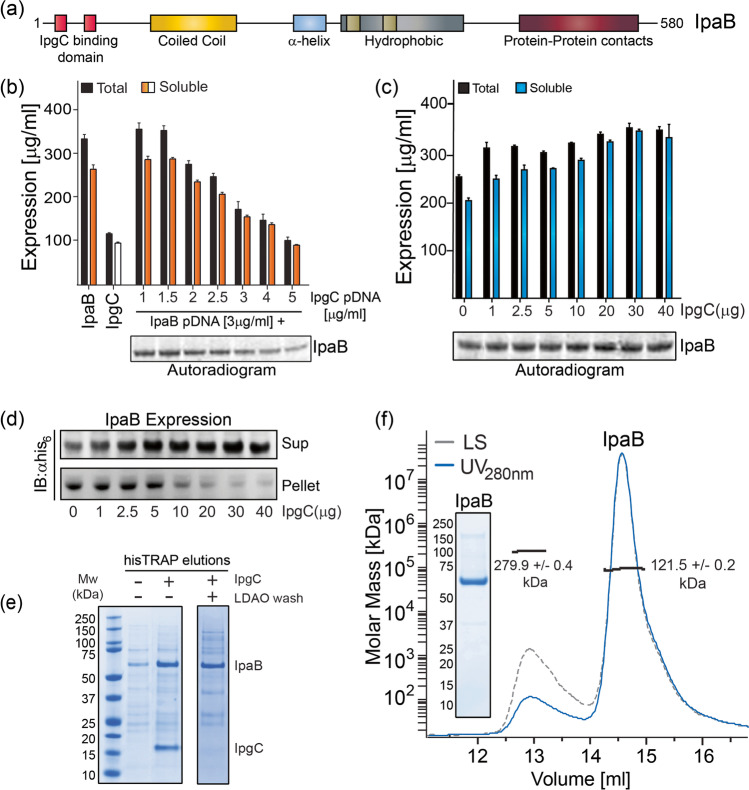
Expression, purification, and biophysical characterization of IpaB. a Modular architecture of IpaB indicating IpgC binding domains near the N-terminus. IpaB co-expressed with IpgC in CFPS reaction containing increasing amounts of IpgC pDNA (b) and IpaB expressed alone when increasing amounts of purified IpgC were added to the CFPS reaction (c); protein amount was determined using 14C-leucine incorporation and data represent mean protein concentration ± SD from 3 independent measurements. d Western blot analysis of the supernatant and pellet fractions from co-expression of IpaB with increasing amounts of purified IpgC in scaled up thin-layer reactions shows complete recovery of IpaB into the soluble fraction when > 30 μg of IpgC was added. e SDS-PAGE analysis shows significantly higher amounts of IpaB recovered in the elution fractions when purified IpgC was exogenously added into the reaction mixture (f) SEC-MALS analysis of purified IpaB (inset, > 95% purity as assessed by SDS-PAGE analysis) shows primarily dimeric state of the protein in solution.