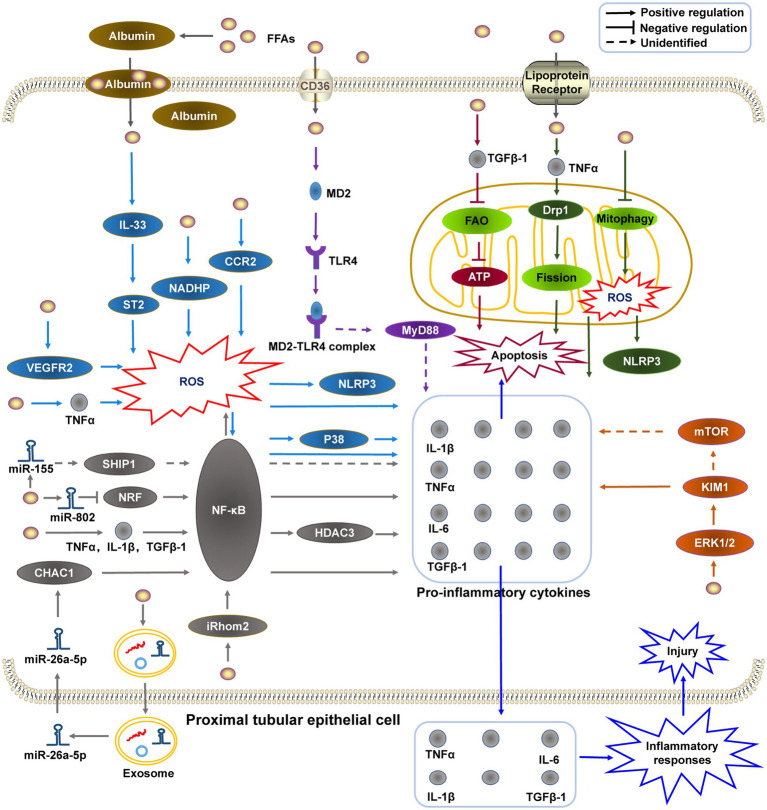
Figure 1.
The potential mechanisms of HFD-induced renal proximal tubular epithelial cell inflammatory injury. (1) HFD promotes the generation of pro-inflammatory molecules by stimulating the MD2-TLR4 complex to recruit MyD88; (2) HFD-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is related to mitochondrial FAO impairment, mitophagy deficiency, and dynamic change; (3) KIM-1 may be upregulated by HFD-activated ERK1/2, and promotes the release of pro-inflammatory molecules directly or indirectly through the mTOR-related pathway; (4) HFD induces NF-κB activation via different pathways (e.g., miRNAs), and subsequently upregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines; and (5) Oxidative stress participate in HFD-induced PTEC inflammatory injury via different pathways. HFD, high-fat diet; MD2-TLR4, myeloid differentiation molecule 2–toll like receptor 4; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; KIM-1, kidney injury molecule 1; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; and miRNAs, micro RNAs.