Figure 1.
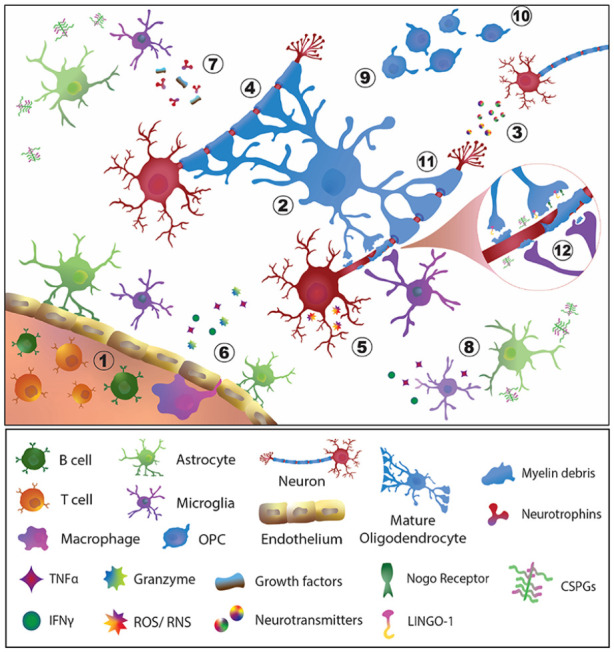
Neurodegenerative and inflammatory processes in an MS lesion amenable to preventive and regenerative therapies. Feasible points of intervention include: (1) immunomodulation, the predominant strategy of currently available therapeutics for MS; (2) promote the viability of OPCs and oligodendrocytes; (3) preserve the quantity and integrity of neurons and axons; (4) Protect myelin to prevent further loss; (5) reduce oxidative stress, apoptosis or cellular dysfunction of neurons and glial cells; (6) promote blood–brain barrier integrity; (7) stimulate neurotrophin and growth factor production; (8) reduce pro-inflammatory activation of glial cells; (9) promote the proliferation of OPCs and their differentiation into mature myelinating oligodendrocytes; (10) induce the migration and recruitment of OPCs and oligodendrocytes to sites of demyelination; (11) induce the formation of new myelin; and (12) target inhibitory factors associated with myelin debris and promote its clearance to support remyelination of denuded axons.
CSPGs: chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans; IFNγ: interferon gamma; LINGO-1: leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobin-like domain-containing protein 1; Nogo: neurite outgrowth inhibitory protein; OPC: oligodendrocyte precursor cell; ROS: reactive oxygen species; RNS: reactive nitrogen species; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha.
