FIGURE 6.
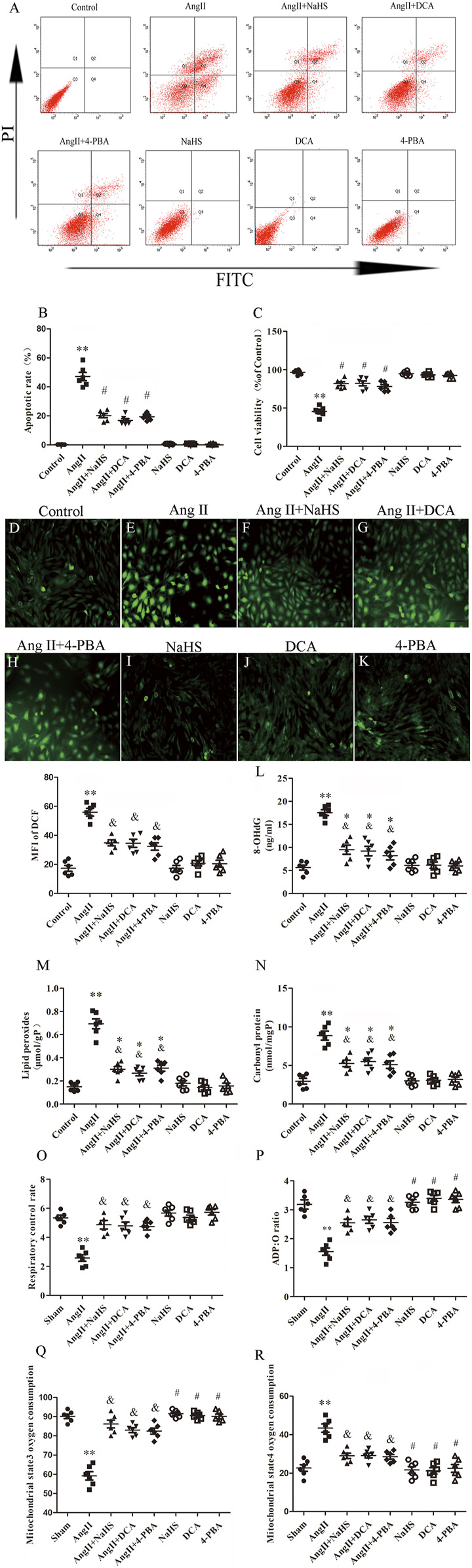
NaHS inhibits HL-1 oxidative stress induced by Ang II and is associated with attenuation of the Warburg effect and ERS. (A) Red staining with representative flow cytometry and quantification of the HL-1 cell apoptotic rate (B) were used as indication treatments (n = 6 in each group). (C) CCK-8 was used to detect the changes in HL-1 cell viability induced by the indicated treatments (n = 6 in each group). After different treatments, ROS were measured using DCFH-DA staining followed by photofluorography (n = 6 in each group, scale bar = 50 μm) and quantitative analysis of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in each group. (D) Control, (E) Ang II, (F) Ang II + NaHS, (G) Ang II + DCA, (H) Ang II + 4-PBA, (I) NaHS, (J) DCA and (K) 4-PBA. 8-OHdG (L), lipid peroxides (M) and Carbonyl protein (N) were determined by kit analysis in the HL-1 cell of the indicated groups (n = 6 in each group). Mitochondrial oxygen consumption was measured using a Clark-type oxygen electrode to detect (O) The respiratory control rate (RCR), (P) The ADP/O ratio, (Q) The mitochondrial state3 oxygen consumption, (R) The mitochondrial state4 oxygen consumption in the HL-1 cell of the indicated groups (n = 6 in each group)**p < 0.01 VS Control, *p < 0.05 VS Control, and p < 0.05 VS Ang II, #p < 0.01 VS Ang II. Groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (Tukey’s) in (D–R), Fisher’s exact test was used to compare groups in (B,C).
