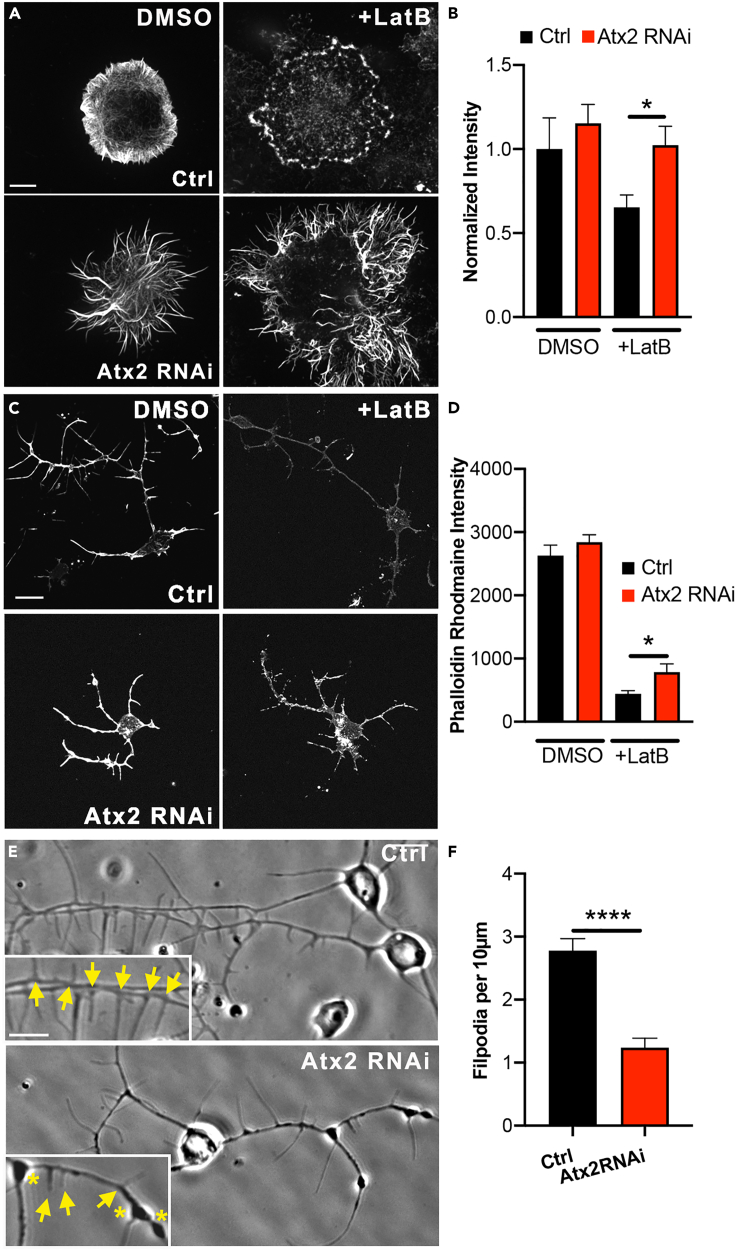
Figure 2.
Ataxin-2 depletion stabilizes the actin cytoskeleton
(A and B) (A) Example images showing phalloidin staining for F-actin in control and Atx2 RNAi treated Drosophila S2 cells treated with DMSO or 10 μM LatB for 1hr. Scale bar, 10 μm (B). Normalized Phalloidin Rhodamine signal (Control = 1.00 ± 0.19, Atx2 RNAi = 1.15 ± 0.11, Control + LatB = 0.65 ± 0.07, Atx2 RNAi + LatB = 1.02 ± 0.11, n = 15–24 cells, p = 0.03).
(C) Example images showing phalloidin staining in control and elav > Atx2 RNAi neurons treated with DMSO or 10 μM LatB for 1hr. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(D) Quantification of Phalloidin Rhodamine intensity along length of neuron (Signal Intensity Control LatB = 440.4 ± 53, n = 37 cells, Signal Intensity Atx2 RNAi LatB = 786.5 ± 128, n = 27 cells, p = 0.02).
(E) Example phase-contrast images showing filopodia from neuronal processes in control and elav > Atx2 RNAi neurons. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(F) Average number of filopodia per 10μm process length (Control = 2.8 ± 0.19, n = 28 cells, Atx2 RNAi = 1.2 ± 0.15, n = 28 cells, p < 0.0001). Data are presented as mean ± standard error. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.