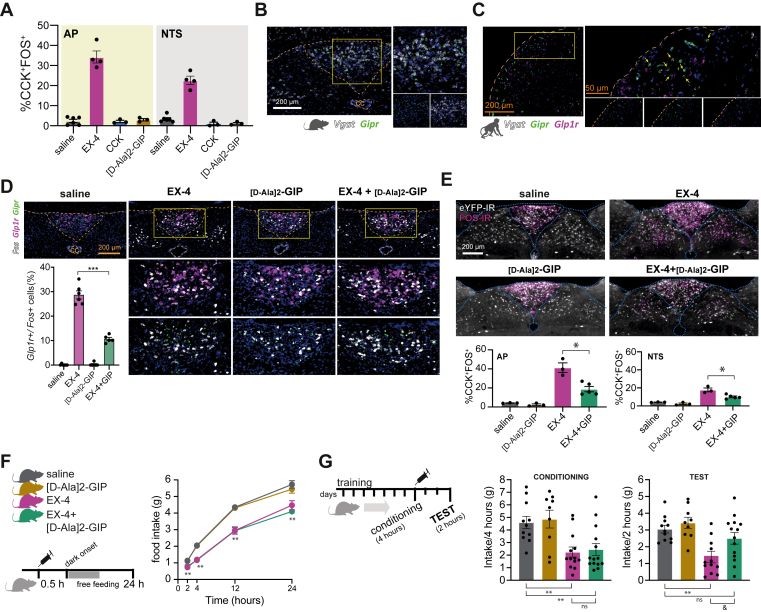
Figure 4.
GIPR agonism reduces the recruitment of Glp1r/CCKAP/NTSneurons and the conditioned taste avoidance elicited by Exendin-4. (A) Quantification of CCKAP/NTS neurons expressing FOS following an injection of EX-4, CCK, or [D-Ala2]-GIP (10, 10, and 100 μg kg−1, IP). (B) FISH labeling of endogenous Gipr and Vgat mRNA in the AP of the mouse. (C) FISH labeling of endogenous Glp1r, Gipr, and Vgat in the AP of the Cynomolgus monkey. (D) Representative FISH labeling and quantification of endogenous Gipr, Glp1r, and Fos mRNAs in the mouse AP following EX-4 (30 kg−1, IP) and [D-Ala2]-GIP (100 μg kg−1, IP) alone or in combination (n = 5–6; F(3, 19) = 222.9, p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA. Post hoc ∗∗∗p < 0.0001). (E) Quantification of CCKAP/NTS neurons expressing FOS following EX-4 and [D-Ala2]-GIP alone, or in combination (n = 3–5; AP: F(3, 10) = 30.73, p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA; NTS: F(3, 10) = 29.17, p < 0.0001. Post hoc ∗p < 0.001).(F) Effect of EX-4 and [D-Ala2]-GIP alone or in combination on food intake (n = 8–9; Treatment: F(3, 31) = 21.91, p < 0.0001; Time: F(1.853, 57.43) = 1214, p < 0.0001; Interaction: F(9, 93) = 7.445, p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA. Post hoc ∗∗p < 0.005) and (G) CTA (n = 9–14; Conditioning: F(3, 43) = 7.176, p = 0.0005, one-way ANOVA. Post hoc ∗∗p < 0.005. Test: F(3, 43) = 6.026, p = 0.0016, one-way ANOVA. Post hoc ∗∗p = 0.0021, &p = 0.0321). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also, Supplemental Fig. 3.