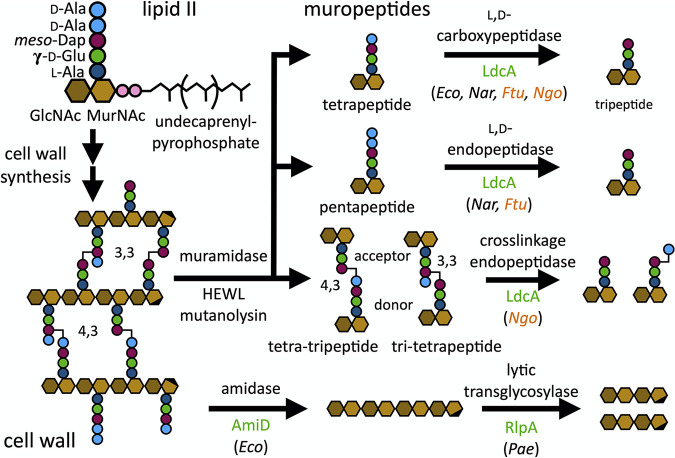
FIG 1.
Schematic representation of the enzymatic activites of previously characterized homologs of the aphid LdcA, AmiD, and RlpA enzymes toward peptidoglycan (PGN). The cell wall is assembled from lipid II, consisting of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc), l-alanine, γ-d-glutamate, meso-diaminopimelic acid (Dap), and d-alanine. Cell wall digestion with muramidase produces muropeptides, many of which are suitable substrates for known LdcA enzyme activities, while AmiD and RlpA act on the polymeric cell wall. Enzyme reactions appear above reaction arrows, while enzyme names are shown below. Enzymes shown in green indicate those for which aphid-encoded homologs exist. Organism abbreviations, shown in parentheses, denote the species for which the reaction has been demonstrated for the enzyme homolog: Eco, E. coli (27, 67); Nar, Novosphingobium aromaticivorans (31); Ftu, Francisella tularensis (29); Ngo, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (30); and Pae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (68). Organism abbreviations shown in orange designate enzymes capable of utilizing both muropeptides and cell wall as substrates.