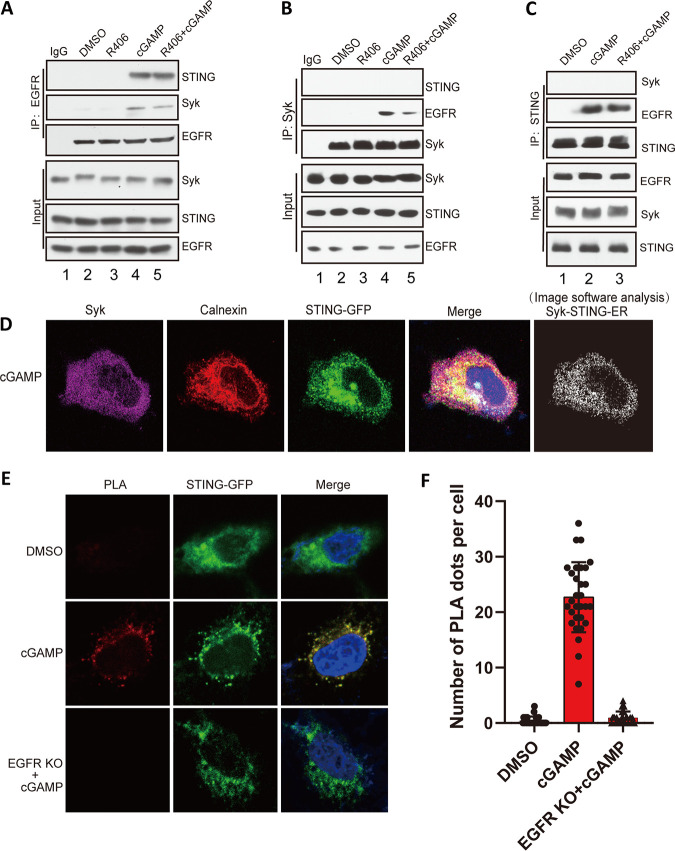
FIG 10.
STING, EGFR, and Syk physically interact in the signaling complex. (A) EGFR interacts with Syk and STING upon cGAMP treatment, and this association does not depend on Syk activity. HT1080 cells were pretreated with R406 for 1 h and treated with cGAMP for 1 h, and the cell lysates were subjected to IP with EGFR antibody and analyzed by WB with Syk, STING, and EGFR antibodies. (B) Syk interacts with EGFR upon cGAMP treatment but not STING. HT1080 cells were pretreated with R406 for 1 h and treated with cGAMP for 1 h, and the cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-Syk and analyzed via WB with the indicated antibodies. (C) STING binds to EGFR, but not Syk, upon cGAMP treatment. HT1080 cells were pretreated with R406 for 1 h and treated with cGAMP for 1 h, and the cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-STING and analyzed via WB with the indicated antibodies. (D) Confocal experiment showed that STING and Syk colocalized on ER. HeLa cells were transfected with mGST-Syk and STING-GFP plasmids, treated with cGAMP for 1 h, fixed, and stained with calnexin (red) and GST antibody (purple). The white dots show STING-Syk colocalization on ER as revealed by Fuji analysis. (E) PLA technology showed that STING and Syk interacted in stimulated cells. The red dots show that STING and Syk were in close proximity. HeLa cells or HeLa EGFR KO cells were transfected with STING-GFP for 24 h, treated with cGAMP for 1 h, fixed, and stained with GFP and Syk antibody followed by PLA. (F) Quantification of PLA dots per cell from panel E (means and SD). P < 0.001. At least 30 cells were quantified from each independent experiment, which was repeated three times with similar results.