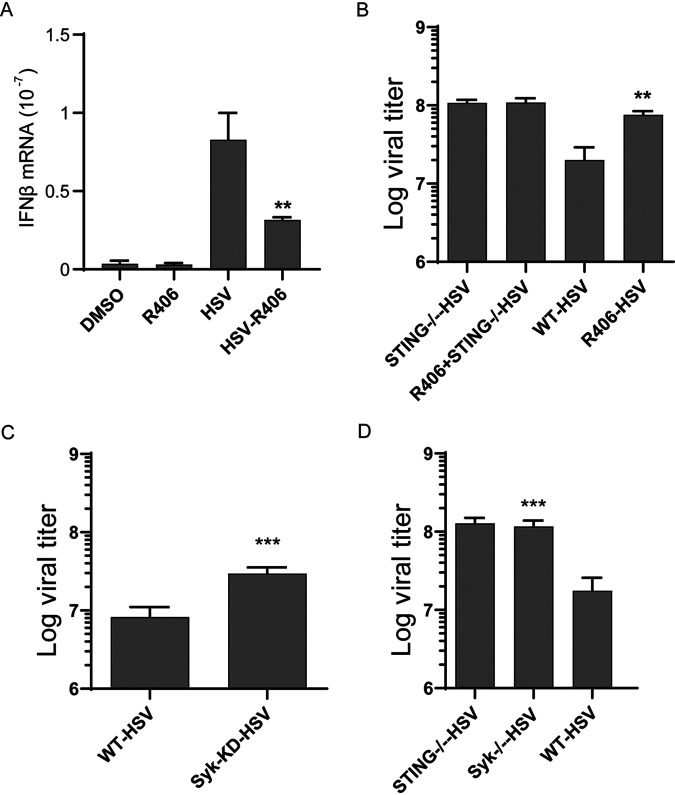
FIG 2.
STING-mediated IFN induction and its antiviral effect on HSV-1 replication require Syk. (A) HT1080 cells were pretreated with R406 for 1 h and infected with HSV-1, RNA was extracted at 4 h postinfection, and IFN-β mRNA induction was measured (n = 3). Bars show means and SD for 3 independent experiments. **, P < 0.01 compared to the HSV-infected group by two-tailed Student’s t test. (B) HT1080 and HT1080 STING−/− cells were pretreated with the Syk inhibitor R406 followed by HSV-1 infection, and viral titers were determined by plaque assays at 16 h postinfection (MOI = 5). Bars show means and SD from 3 independent experiments. **, P < 0.01 compared to the HSV-infected WT group by two-tailed Student’s t test. (C) WT HeLa cells and Syk KD cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI = 5), and viral titers were determined by plaque assays at 16 h postinfection Bars show means and SD from 3 independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001 compared to the HSV-infected WT group by two-tailed Student’s t test. (D) WT HT1080 cells, STING−/− HT1080 cells, and Syk−/− cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI = 5), and viral titers were determined by plaque assays at 16 h postinfection. Bars show means and SD from 3 independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001 compared to the HSV-infected WT group by two-tailed Student’s t test.