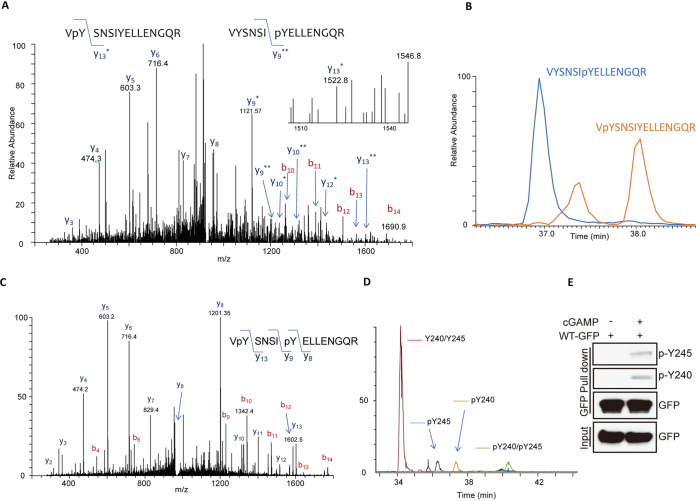
FIG 3.
Tyr240 of STING is phosphorylated upon cGAMP stimulation. (A) After 3 h of cGAMP stimulation, STING-GFP was purified from 293XL cells via GFP trap beads, fractionated on an SDS-PAGE gel, and digested with trypsin and chymotrypsin, and the digests were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. A doubly charged peptide with a mass of 932.93 Da was identified in a targeted analysis of GFP-STING. The collision-induced dissociation (CID) spectra for this peptide contains several C-terminal y ions, and the masses of these ions are consistent with the presence of more than one phosphoisoform. The mass difference of the y13* peptide is consistent with modification at Y240, and the mass of the y9** peptide is consistent with modification at Y245. (B) The degree of modification from A was determined by plotting chromatograms for both the unmodified and modified forms of the Y240/Y245 peptides. The chromatograms for the VYSNSIpYELLENGQR and VpYSNSIYELLENGQR peptides are shown. (C) A doubly charged peptide with a mass of 972.911 Da was identified in a targeted analysis of STING-GFP. The CID spectrum for this peptide contains several C-terminal y ions, and the masses of the y8, y9, and y13 ions are consistent with phosphorylation at Y240 and Y245. (D) Chromatograms for the unmodified, pY240, pY245, and pY240-pY245 peptides from STING-GFP WT. The phosphopeptides are several orders of magnitude lower in abundance than the unmodified peptide. (E) Specific antibodies detecting pY240 and pY245 phosphorylation of STING in cGAMP treated 293 XL cells expressing STING-GFP.