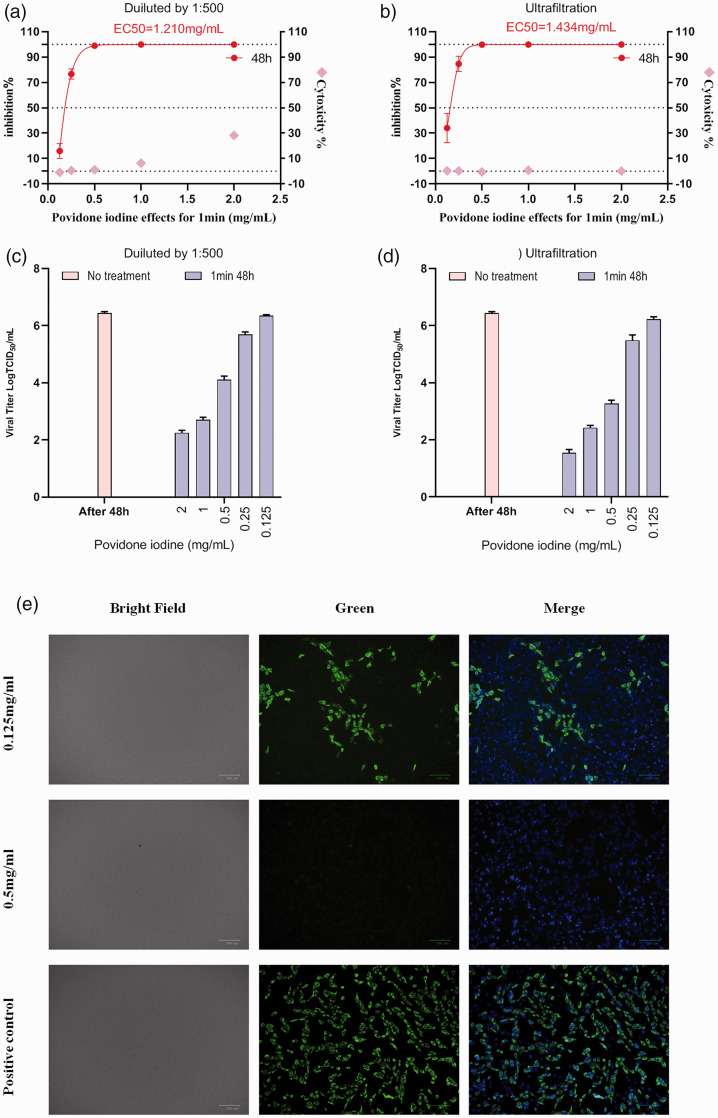
Figure 4.
Antiviral activity, cytotoxicity, viral titre data and immunofluorescence microscopy of Calu-3 cells infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 treated with povidone-iodine (PVP-I) at different concentrations for 1 min. (a) Virus inhibition and cytotoxicity data obtained using different concentrations of PVP-I disinfectant on infected Calu-3 cells using the experimental procedure shown in Figure 1a. (b) Virus inhibition and cytotoxicity data obtained using different concentrations of PVP-I disinfectant on infected Calu-3 cells using the experimental procedure shown in Figure 1b. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the viral RNA load in cell culture supernatant and CCK-8Continued.assays were used to detect the cytotoxicity of PVP-I to Calu-3 cells. The left and right y-axes of the first two graphs show the mean inhibition rate (%) produced by the PVP-I on the virus and the cytotoxicity of the PVP-I on the Calu-3 cells, respectively. (c, d) Calu-3 cells were treated with different concentrations of PVP-I for 1 min and the 50% tissue culture infectious dose assay (TCID50) values were used to determine virus titre using the method of Reed and Muench. 19 Data presented as mean ± SD for three repeated experiments. (e) Immunofluorescence microscopy of Calu-3 cells infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 and disinfected with PVP-I for 1 min at different concentrations. Cells were counterstained with 2-(4-amidinophenyl)-6-indolecarbamidine dihydrochloride to stain the nuclei. Scale bar 100 μm.