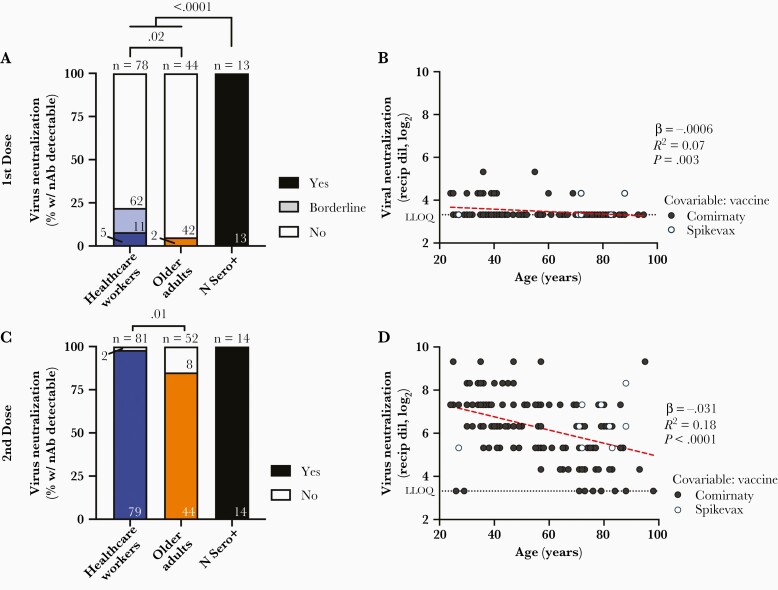
Figure 3.
Viral neutralization activity of vaccine-induced antibodies is weaker in older adults. A, Frequency of COVID-19–naive health care workers (blue) and older adults (orange), as well as convalescent participants (N Sero+; black) are shown as histograms. The proportion of participants in each group who displayed neutralizing activity against live SARS-CoV-2 (USA-WA1/2020 strain) in 3/3 wells at a 1:20 or higher plasma dilution is shown in the darkest color, while those displaying borderline activity (defined as neutralization in least 1 well at a 1:20 dilution) is shown in lighter color. Total number in each group is shown above each bar, with the number of participants displaying each activity shown within the bar. P values computed using Fisher exact test are shown above each comparison. B, Same data as the COVID-19 participants shown in A (where neutralization includes both yes and borderline categories) but plotted by age, and where neutralization is reported as the reciprocal log2 dilution value. Samples that displayed no evidence of neutralization were coded as having a reciprocal dilution factor of 10 (3.32 log2). Symbols are colored by vaccine received, which was significantly associated with neutralization activity after 1 dose (Table 2). Statistics were computed using ordinary least-squares regression. C and D, Same as A and B but for neutralization responses measured 1 month after 2 doses of mRNA vaccine and where neutralizing activity required inhibition of cytopathic effects in 3/3 wells at a 1:20 or higher plasma dilution. Abbreviations: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; LLOQ, lower limit of quantification; Recip dil, reciprocal dilution; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; w/ nAb, with neutralizing antibodies.