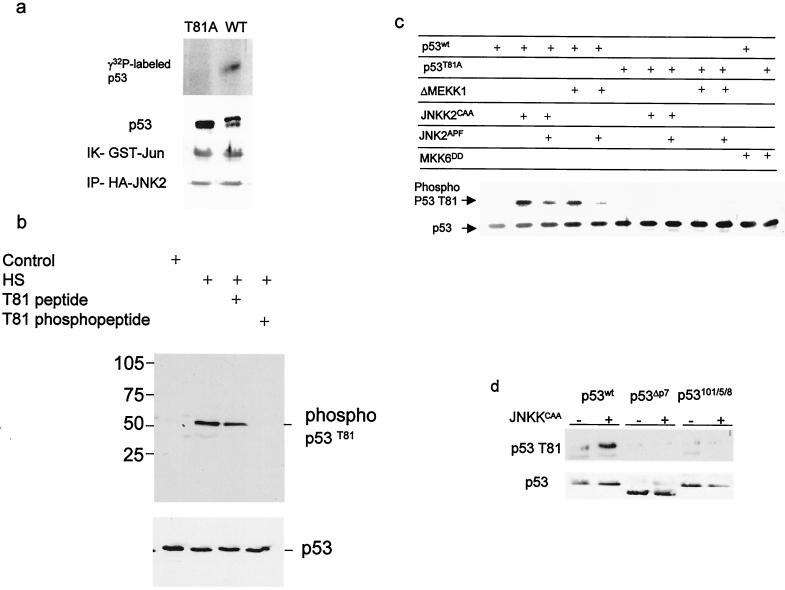
FIG. 1.
JNK phosphorylates p53 on T81. (a) Wild-type or mutant (T81A) forms of human p53 were in vitro translated, purified, and subjected to phosphorylation using JNK immunopurified from UV-treated 293T cells. Middle, immunoblot analysis of material subjected to autoradiography using DO1 antibodies. The doublet represents the nonphosphorylated (lower band) and phosphorylated (upper band) forms of p53. The control reaction using c-Jun as a substrate (immunokinase [IK] reaction of GST-Jun) and the level of HA-JNK2 that was immunoprecipitated (IP-HA-JNK2) are shown (bottom). (b) Proteins prepared from NHF that were exposed to sham stress (control) or heat shock (HS; 42°C for 1 h) were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the antibodies to phosphorylated T81 in the presence of excess phospho or nonphospho peptides as indicated (top) or to Western blotting using DO1 antibodies (bottom). (c) T81 phosphorylation on wt or T81A forms of p53 was monitored after cotransfection of the respective construct (1 μg) with the indicated upstream kinases (3 μg) into H1299 cells. Analysis of T81 phosphorylation was carried out using the antibodies to phospho-T81. Bottom, p53 levels detected with DO1 antibodies. (d) T81 phosphorylation of p53 impaired in JNK association. Either wt rat p53 or p53 with deletions (ΔP7) or mutations (at aa 101, 105, and 108) within the region, which encompasses the JNK binding site (1, 18) was cotransfected with JNK2CAA into H1299 cells. Proteins were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using phospho-T81 antibodies (top) or DO1 antibodies (bottom).