Figure 1.
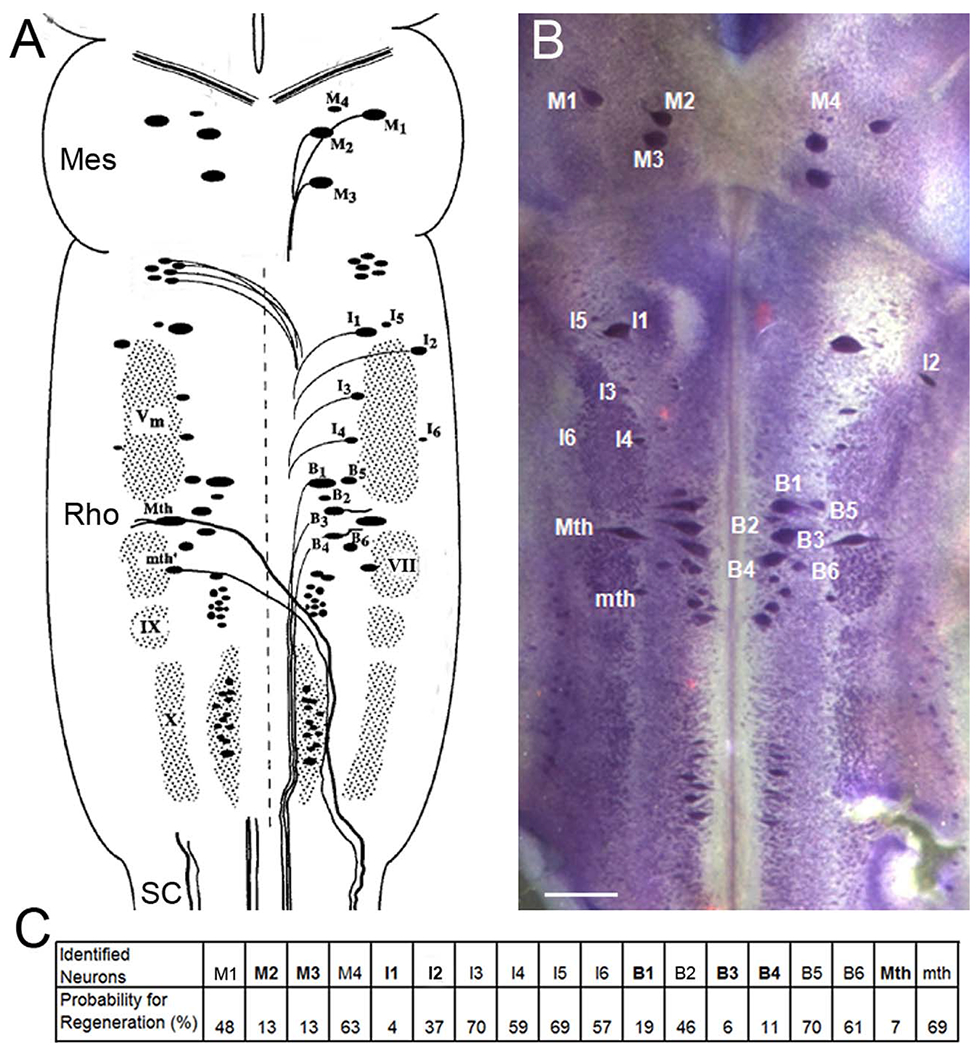
Cytoarchitecture of the identified reticulospinal neurons in lamprey brain. A: The brain of the large larval lamprey is diagrammed to illustrate locations of large individually identified reticulospinal neurons according to the nomenclature of Rovainen (1967) as modified by Swain et al. (1993). These are the Müller and Mauthner neurons, which also will be referred to in subsequent figures. M, mesencephalic Müller cells; I, isthmic Müller cells; B, bulbar Müller cells; Mth, Mauthner cell; mth, auxiliary Mauthner cell; Vm, trigeminal motor nucleus; IX, glossopharyngeal motor nucleus; X, vagal motor nucleus; VII, the facial motor nucleus. A and C are modified from Jacobs et al. (1997), M2, M3, I1, I2, B1, B3, B4, Mth are considered bad regenerators (bolded letters), and the others are good regenerators (Davis and McClellan, 1994; Jacobs et al., 1997). Mes, mesencephalon; Rho, rhombencephalon; SC, spinal cord. B: The brain of a large larval lamprey was stained with toluidine blue to show those identified reticulospinal neurons. C: The probability of axon regeneration for each identified reticulospinal neuron was determined by applying HRP 5 mm caudal to original lesion at 10 weeks after SC transection. Scale bar = 250 μm in B.
