FIG. 9.
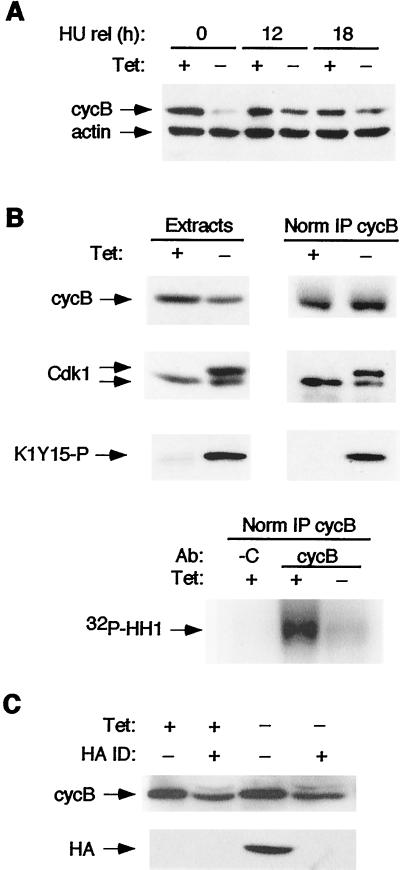
Cdk2-dn-expressing cells arrest in G2 phase with moderately reduced levels of cyclin B and greatly reduced activation of Cdk1. Dn.4 cells were synchronized with HU and then nocodazole, with or without Cdk2-dn induction, as described in the legend to Fig. 8. Protein extracts were subjected to immunoblotting, with or without the following immunoprecipitations. (A) Cyclin B (cycB) levels in S and G2/M phases are moderately reduced by Cdk2-dn induction. Extracts were prepared from cells at the end of treatment with HU (0 h) and at 12 h and 18 h after release (rel) into nocodazole and subjected to immunoblotting for cyclin B and actin (loading control). Note that cyclin B levels are strongly reduced by Cdk2-dn induction during the G1/S block but only moderately reduced, compared to uninduced cells, at the G2/M block. (B) Cdk1 activation is inhibited by Cdk2-dn induction. (Top) Immunoblotting was performed on the 18-h extracts (left), normalized by protein content, or cyclin B immunoprecipitates (right), normalized for immunoprecipitated cyclin B (IP cycB), using anti-cyclin B, Cdk1, and K1Y15-P antibodies. (Bottom) Kinase activity associated with the normalized cyclin B immunoprecipitates was assayed using histone H1 (HH1) as a substrate. C denotes immunoprecipitation with a negative control antibody (Ab). (C) Cdk2-dn does not sequester cyclin B. Cdk-2dn was immunodepleted (ID) from the above extracts, and the levels of cyclin B (top) and Cdk2-dn (detected through its HA tag; bottom) remaining in the supernatant were assayed by immunoblotting.