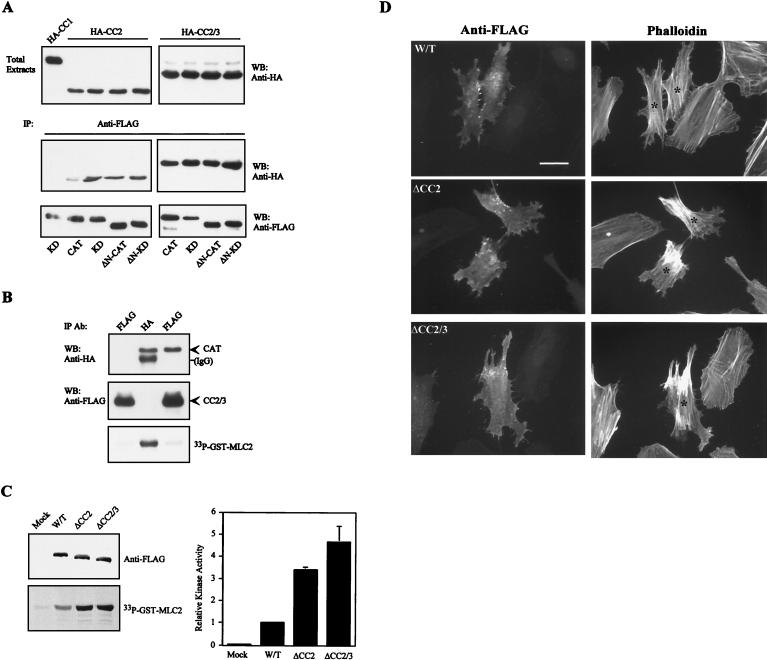
FIG. 7.
Interaction between the distal CC domains and the kinase domain causes MRCKα kinase inhibition. (A) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with a pXJ40 vector containing HA-CC2 or HA-CC2/3 (Fig. 3), together with each of the various FLAG-tagged MRCKα kinase domain constructs, as indicated (bottom). Immunoprecipitations (IP) were carried out with anti-FLAG antibody, and the IP products were Western blotted (WB) with anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibodies. Expressions of the HA-tagged CC domains in total extracts are shown at the top, and HA-CC1 was used as the negative control. (B) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-CC2/3 alone (left lane), HA-CAT alone (middle lane), and FLAG-CC2/3 together with HA-CAT (right lane). IP were carried out using either anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies as indicated, and the products were subjected to kinase assays using GST-MLC2 as the substrate. The immunoprecipitated products recovered were immunoblotted with anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibodies (Ab). IgG, immunoglobulin G. (C) COS-7 cells expressing the FLAG-tagged deletion mutant forms ΔCC2 (MRCKα-ΔCC2Δ750–809 and ΔCC2/3 (MRCKα-ΔCC2/3Δ750–938) were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and assayed for kinase activities toward GST-MLC2 (left). The GST-MLC2 phosphorylation levels shown are means and standard errors of activities relative to that of wild-type (W/T) MRCKα (right). (D) Effects of the expression of CC deletion mutant forms on actin filament rearrangement in HeLa cells. Transfected cells with the various wild-type and mutant constructs were doubly stained with anti-FLAG antibody to show transfected cells (left) and with phalloidin to show actin filaments (right). Transfected cells are marked with asterisks. Scale bar = 10 μM.