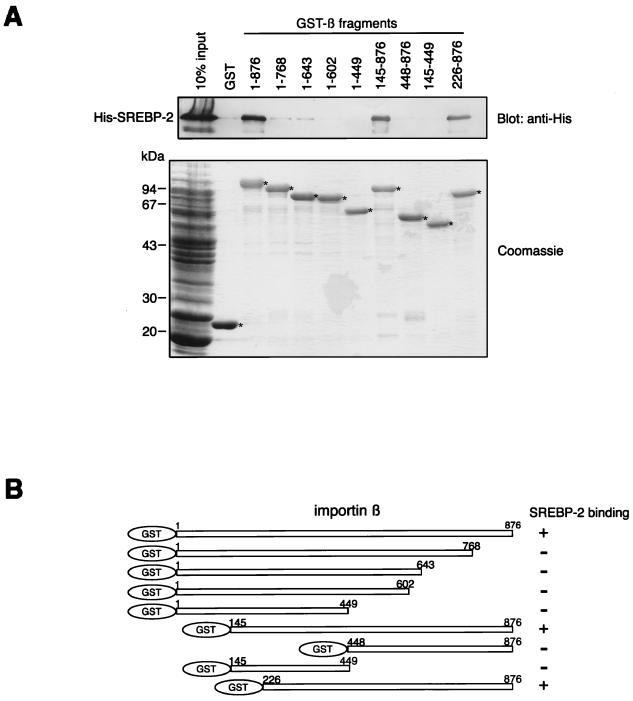
FIG. 1.
Mapping of the SREBP-2 binding domain of importin β. (A) Full-length (1 to 876) and various truncated mutants of importin β were produced as GST fusion proteins and tested for their ability to bind to SREBP-2. Purified GST or GST-importin β fragments (150 pmol) were incubated with 270 μl of E. coli lysate expressing His-SREBP-2 (300 μl final volume). GST fusion proteins were then absorbed to 15 μl of glutathione-Sepharose beads. After extensive washing, the bound proteins were eluted by boiling in SDS-PAGE sample buffer and divided into two equal portions. Each portion was separated by SDS–10% PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using the monoclonal anti-penta-His antibody (top) or by Coomassie staining (bottom). E. coli lysate (13 μl) expressing His-tagged SREBP-2 was directly applied to each gel (10% input). Asterisks indicate the positions of the GST and GST-importin β fragments which were absorbed to the glutathione-Sepharose beads (bottom). (B) Schematic representation of the importin β deletion mutants used in this study. All mutants were expressed as GST fusion proteins. Numbers indicate the amino acid position of each importin β fragment.