FIGURE 3.
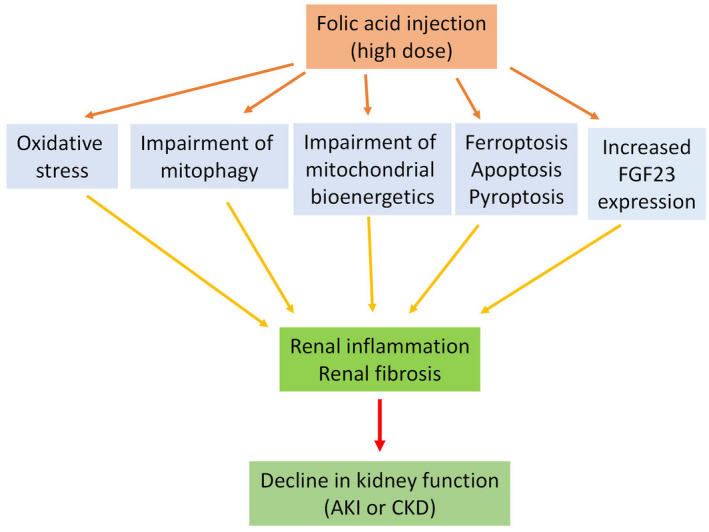
Major pathological mechanisms of folic acid (FA)‐induced acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). These include oxidative stress, impairment of mitophagy and mitochondrial bioenergetics, ferroptosis, apoptosis and pyroptosis as well as increased expression of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23). These mechanisms together result in renal inflammation and renal fibrosis, eventually leading to renal dysfunction or kidney disease. Please note that this figure and this article do not mean to exhaust all the mechanisms implicated in FA‐induced kidney disease
