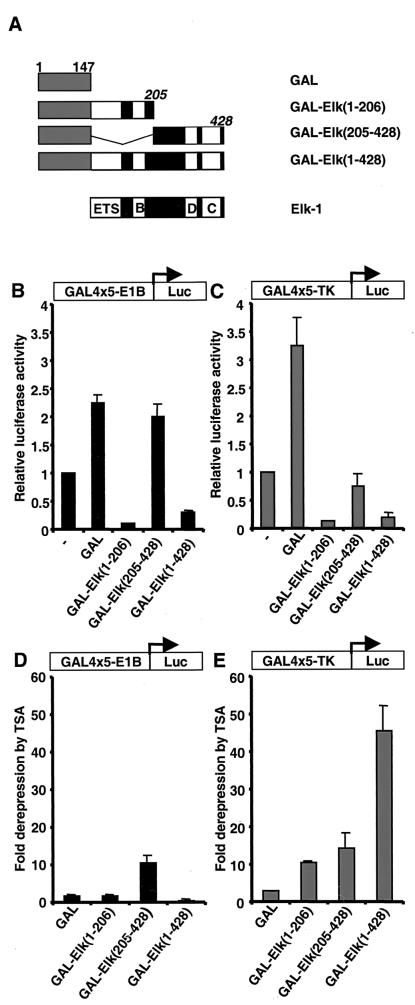
FIG. 1.
Elk-1 contains a transcriptional repression domain. (A) Diagram illustrating a series of truncated Elk-1 proteins (black boxes, with domains indicated by white boxes) fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (amino acids 1 to 147, grey boxes). Numbers of the C-terminal amino acids in the Elk-1 moiety are indicated (italics). (B and C) GAL-Elk fusion proteins repress GAL4-driven luciferase re- porter genes. 293 cells were cotransfected with 0.1 μg of CMV promoter-driven constructs encoding the indicated GAL4–Elk-1 derivatives and 1 μg of GAL4-driven luciferase reporter plasmids containing the minimal E1B (B) or TK (C) promoter. Cells were maintained in serum-free conditions throughout the experiment. The layout of the reporters is represented as a diagrammatic insert. Luciferase activities relative to the control cells (without transfection of any GAL4 fusions [—]) are presented (means ± standard deviation, n = 2). (D and E) TSA sensitivity of the indicated reporters in the presence of GAL-Elk fusion proteins. Transfection assays were carried out as above. Cells were left in serum-free medium after transfection, treated or not with TSA, and harvested 18 h later. Luciferase activities relative to the untreated cells (fold derepression) are presented (means ± standard deviation, n = 2).