Fig. 3.
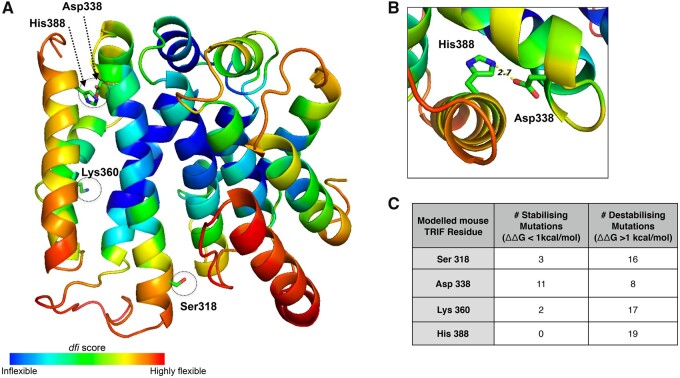
In silico analysis highlights the structural importance of sites under positive selection in mTRIF. (A) The predicted structure of a portion of the mTRIF protein (residues Pro110 to Gln394) generated using MODELLER (Fiser and Sali 2003). Residues are highlighted based on their dynamic flexibility index, (dfi) score, as per the indicated scale, and the position of four mouse residues under positive selection are indicated. (B) A close up of His 388 and Asp 338, two mTRIF residues under positive selection, in the predicted TRIF protein structure. The shortest distance between their two side chains is indicated (2.7 Å) and suggests a potential interaction between these two residues. Both (A) and (B) were generated using pymol (Delano 2002). (C) A summary of the in silico mutagenesis analysis done on mTRIF protein structure using dezyme software (https://soft.dezyme.com). The number of mutations that led to either a decrease (stabilizing) or increase (destabilizing) in the folding free energy (△△G) of mTRIF is indicated.