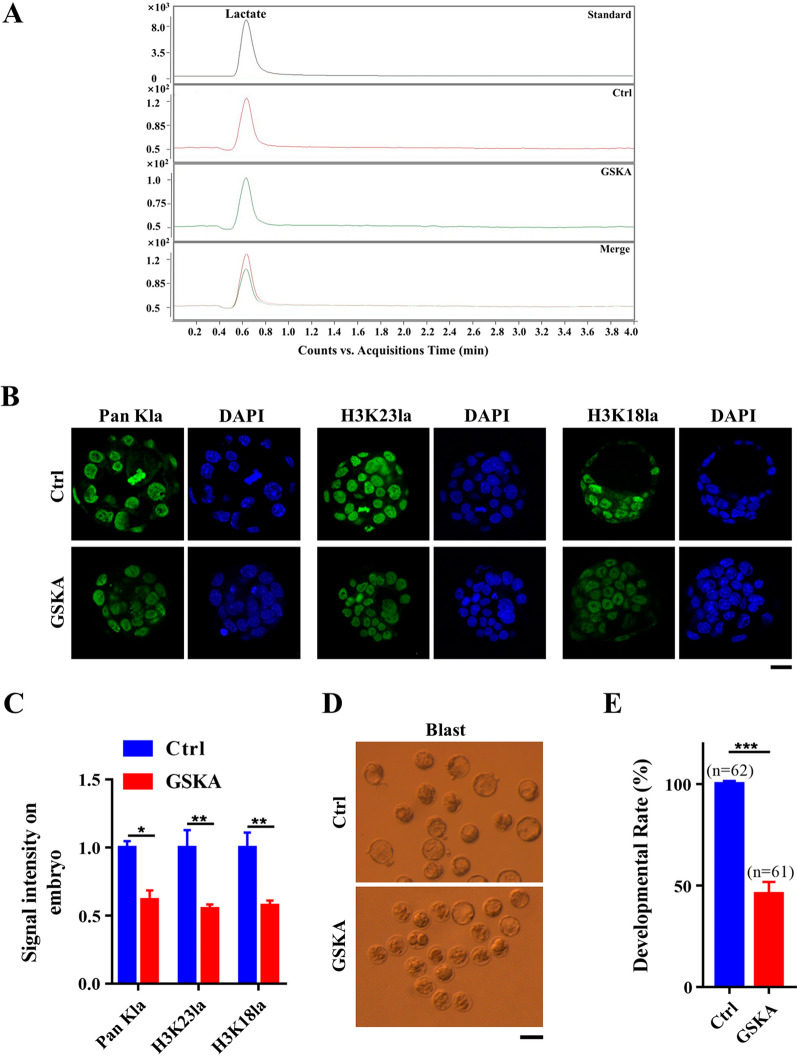
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of LDHA activity was detrimental for pre-implantation embryonic development. a UPLC–MS chromatogram of endogenous lactate extracted from NIH3T3 cells after 48 h treatment with DMSO or GSKA. b GSKA treatment led to reduced pan histone lactylation, H3K23la and H3K18la in the blastocysts. Morula stage embryos (72 hpi) were cultured with 100 pmol of GSKA (LDHA inhibitor) or the same concentration of DMSO (Ctrl) for 1 h, then transferred to fresh medium and cultured till blastocyst stage. Representative immunofluorescence staining of the pan histone lactylation (Green), H3K23la (Green) and H3K18la (Green) in blastocyst stage embryos were shown. DNA was stained with DAPI (Blue). Scale bars: 20 μm. c Quantification of fluorescence intensity for pan histone lactylation, H3K23la and H3K18la in embryonic blastomeres (n = 30 blastomeres per group, 3 independent experiments). d Representative images of blastocysts (Blast) treated with DMSO (Ctrl) or GSKA (GSKA). More than 10 embryos were examined in each stage of each condition. Scale bars: 50 μm. e Quantification of developmental rate of embryos treated with DMSO (Ctrl) or GSKA (GSKA) at the morula stage (n = 62 cells in ctrl group; n = 61 cells in GSKA group, 3 independent experiments). Error bars indicated SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. ⁎p < 0.05; ⁎⁎p < 0.01; ⁎⁎⁎ p < 0.001