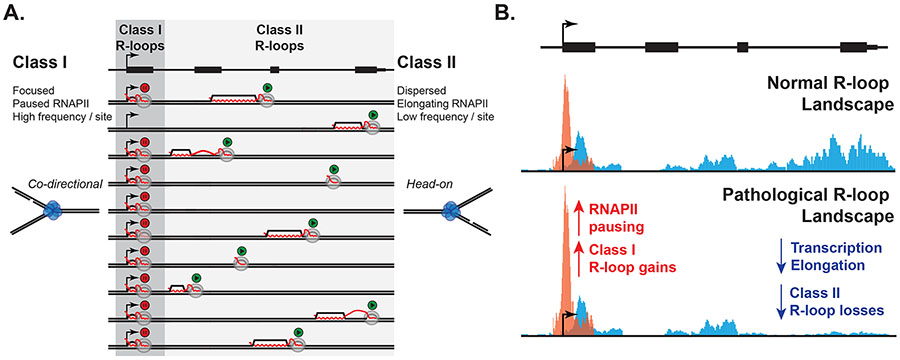
Figure 2. Pause-associated R-loops as candidate harmful R-loops.
A. Schematic of a gene and its hypothetical R-loop formation state in 10 independent chromosomes. Class I R-loops are suggested to frequently arise at promoters as a result of promoter-proximal pausing. By contrast, elongation-associated Class II R-loops are spread throughout the gene body and therefore occur at much lower frequencies at any given site. RNA is only depicted when in a R-loop bound state or exiting RNAP (full transcript not shown). B. Under pathological conditions caused for instance by defective mRNA processing, RNAPII pausing is proposed to increase, causing a focal increase in Class I R-loops. Class II R-loops are by contrast proposed to be reduced as a result of lower transcription initiation due to increased pausing. Under such conditions, paused RNAPII complexes anchored to Class I R-loops may represent significant obstacles to replication fork progression, causing DNA damage.