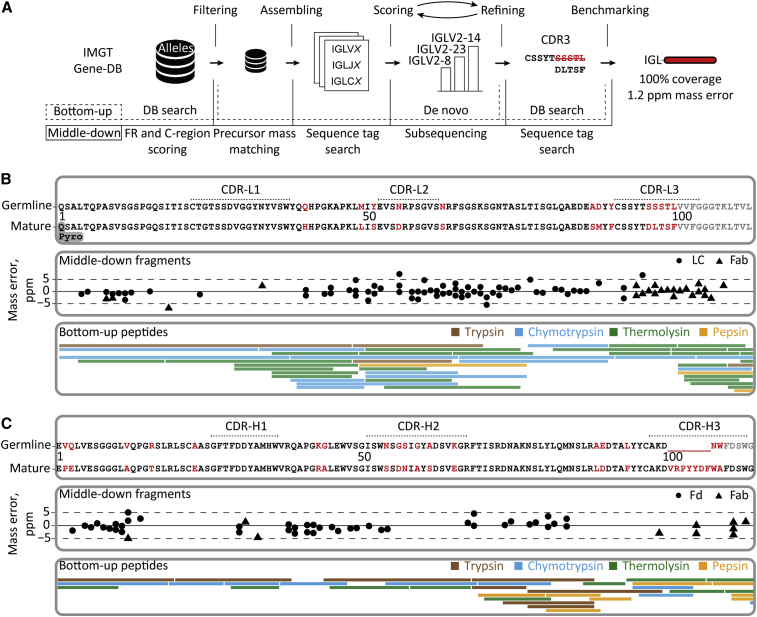
Figure 4.
Integrative de novo sequencing of the Fab clone 24.4 1 47,359.4 from donor F59 combining middle-down and bottom-up MS data
(A) Data analysis pipeline displaying the key steps in the de novo sequencing, namely, filtering of the germline database of light- and heavy-chain sequences, assembling of selected allelic variants with mass constraints, scoring of the assembled sequences by using middle-down MS data, iterative refining of the best scoring templates by using peptides in bottom-up MS, and benchmarking of the optimized mature sequences using data from both middle-down and bottom-up MS analysis.
(B) Alignment of the best matching germline IGLV amino acid sequence from the IMGT database (IGLV2-14∗01) with the mature sequence that was determined for the light chain of the dominant clone (top box), the fragments from middle-down MS (middle box), and the peptides from bottom-up MS.
(C) Alignment of the best matching germline IGHV amino acid sequence from the IMGT database (IGHV3-9∗01) with the mature sequence that was determined for the Fd of donor F59’s clone 24.4 1 47,359.4 (top box), the fragments from middle-down MS (middle box), and the peptides from bottom-up MS. CDR regions in top panels of (B) and (C) were annotated with reference to the closest matching IMGT sequence. Amino acids that were determined to be different in the mature 24.4 1 47,359.4 sequence are highlighted in red.