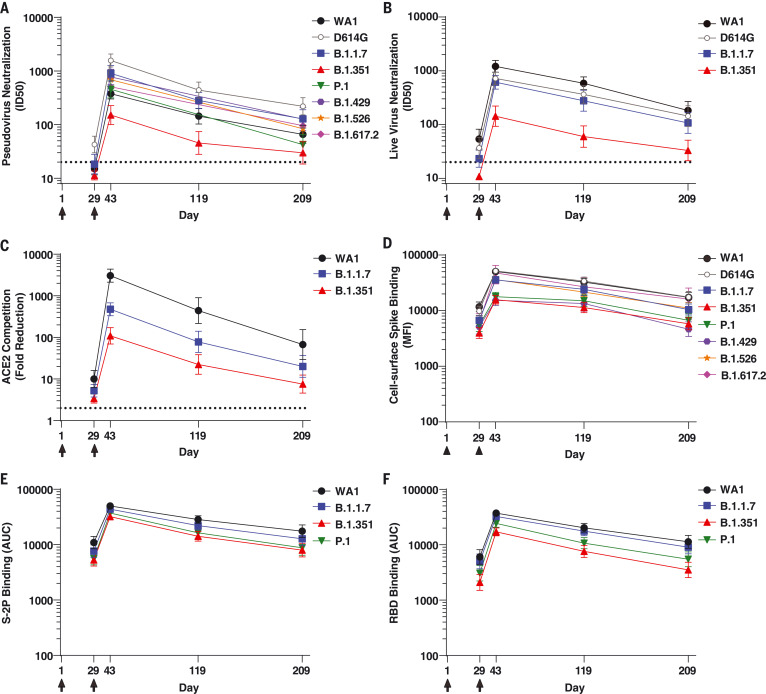
Fig. 1. Binding and functional antibodies persist for 6 months after the second dose of the mRNA-1273 vaccine.
(A) Pseudovirus neutralization, expressed as 50% inhibitory dilution (ID50). Dotted line indicates the limit of detection (>20). Pseudoviruses included WA1, D614G, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1, B.1.429, B.1.526, and B.1.617.2. (B) Live-virus FRNT neutralization, expressed as ID50. Dotted line indicates the limit of detection (>20). Viruses included WA1, 83E (spike is D614G), B.1.1.7, and B.1.351. (C) Competition of ACE2 binding to RBD, measured by MSD-ECLIA and expressed as fold reduction of ACE2 binding in the presence of serum compared with no-serum control. Dotted line indicates the limit of detection (>2). RBD proteins included WA1, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351. (D) Binding to cell surface–expressed full-length spike, measured by flow cytometry and expressed as median fluorescence intensity (MFI). Spikes included WA1, D614G, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1, B.1.429, B.1.526, and B.1.617.2. (E) Binding to soluble spike protein S-2P, measured by MSD-ECLIA and expressed as area under the curve (AUC). S-2P proteins included WA1, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1. (F) Binding to RBD protein, measured by MSD-ECLIA and expressed as AUC. RBD proteins included WA1, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1. For all assays, sera from n = 24 individuals were sampled at four time points. Individuals were vaccinated with 100 μg mRNA-1273 at days 1 and 29 (arrows). Symbols show the geometric mean value, and error bars show 95% confidence intervals.