FIG. 2.
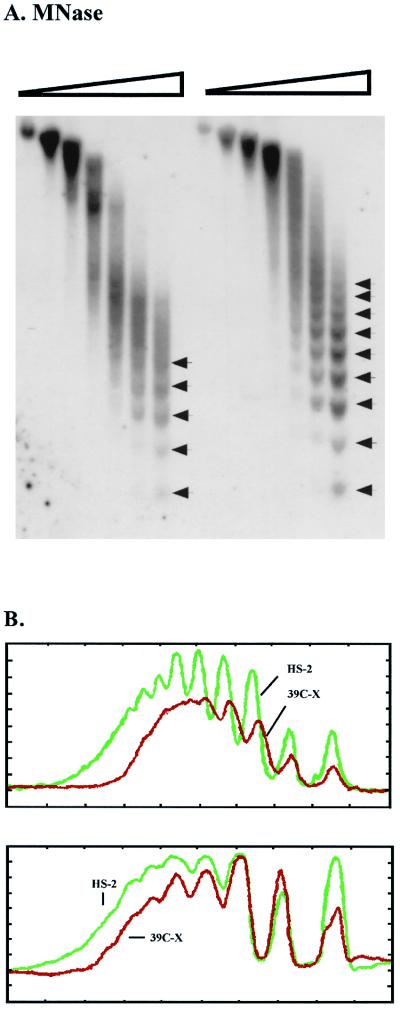
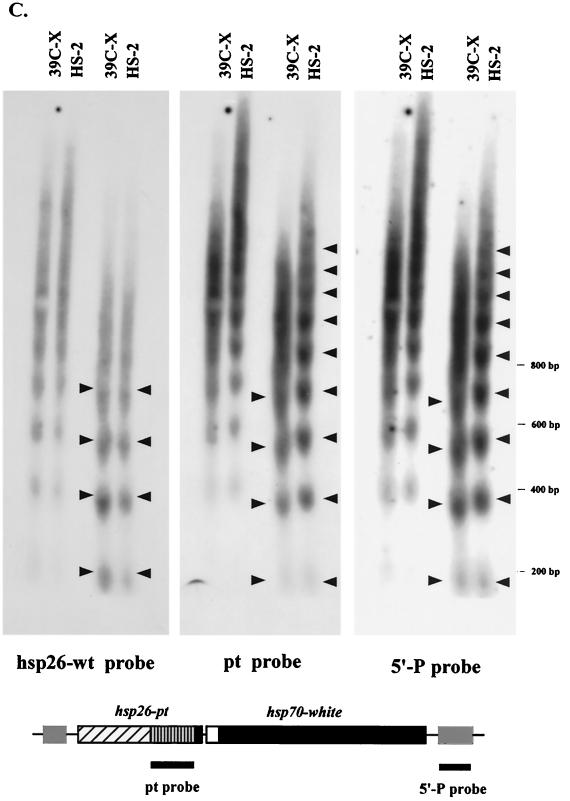
MNase digestion reveals long-range nucleosomal ordering, with an altered repeat size, at the silenced transgene. (A) Nuclei isolated from 6- to 18-h-old embryos from lines 39C-X and HS-2 were treated with increasing amounts of MNase (concentrations of 0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.08, 0.12, and 0.24 U/μl), and the DNA was purified and run in a 1.5% agarose gel. The DNA was transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane, and the membrane was hybridized with α-32P-labeled pt fragment. Linker sites cleaved by MNase are indicated by arrows. (B) Densitometric scans from the last lane of each sample set are compared (top to bottom of each lane is left to right along the x axis), aligned at the position of the mononucleosome (top panel). The same blot used in panel A was stripped and rehybridized with a 0.8-kb PvuII-SacII fragment from the 3′ coding region of the endogenous hsp26 gene as a control panel. Densitometric scans from the last lane of this sample set are shown (bottom (data not shown)). (C) The DNA samples used for the last two lanes of each set in panel A were run in parallel on a 1.8% agarose gel. The blot was hybridized with the 0.8-kb PvuII-SacII fragment from the endogenous hsp26 coding region (left), stripped, and rehybridized with the pt DNA fragment (center) or with a fragment from the 5′ end of the P element (right). The positions of molecular size markers are indicated to the right of the gels. The map below the gels indicates the probes used for the center and right panels.