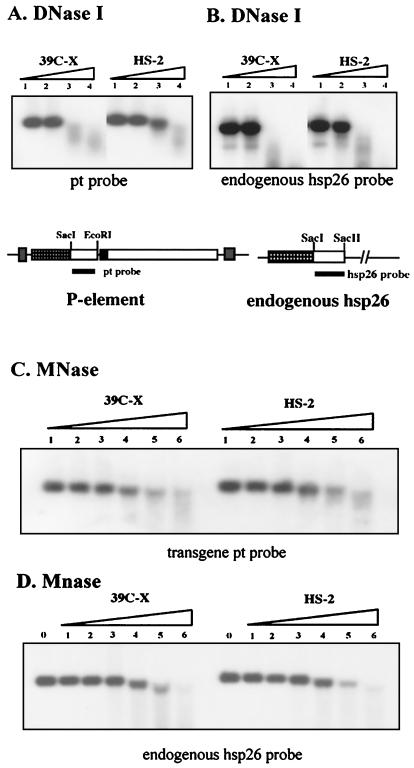
FIG. 4.
A nucleosome array in heterochromatin is resistant to digestion with DNase I, but not with MNase. (A) Nuclei from 6- to 18-h-old non-heat-shocked embryos (lines 39C-X and HS-2) were treated with DNase I at concentrations of 0.016, 0.032, 0.064, or 0.128 U/μl. Purified DNA was then cut with SacI and EcoRI, and the presence of the 1-kb restriction fragment was monitored using Southern blotting with the pt DNA fragment as a probe. (B) In the control experiment, the digested DNA was cut with SacI and SacII, and a 0.8-kb DNA fragment from the 3′ portion of the endogenous hsp26 gene was used as a probe. (C) An analogous experiment used MNase at concentrations of 0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.08, 0.12, and 0.24 U/μl to digest the chromatin in nuclei. The pt DNA fragment was used as a probe. (D) The control experiment performed as described above for panel B to monitor disappearance of the SacI-SacII fragment of the endogenous hsp26 gene shows that digestion of the chromatin from the two lines occurred at the same rate.