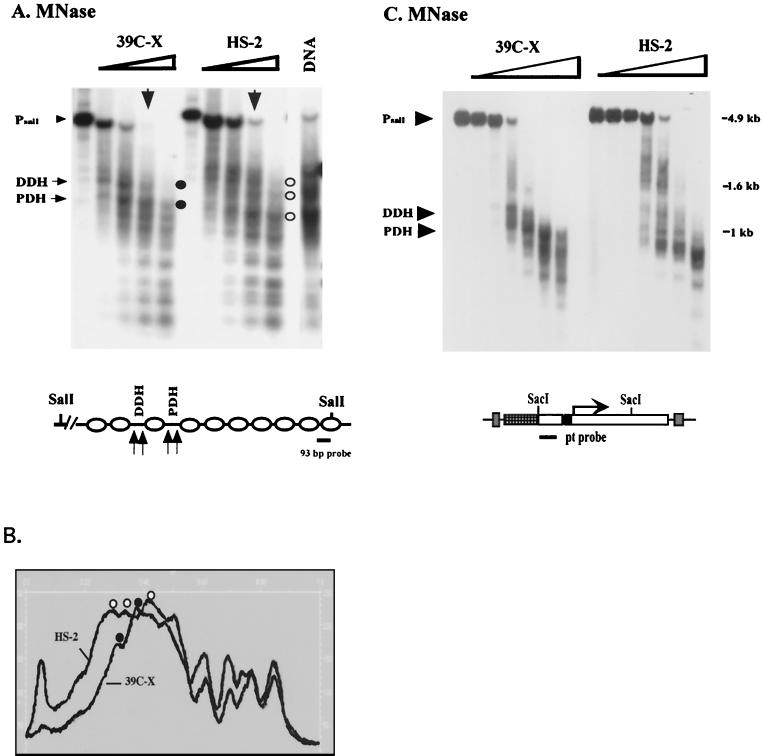
FIG. 5.
Mapping nucleosome positions in the heterochromatic transgenes using the indirect end labeling technique. (A) Nuclei isolated from 6- to 18-h-old embryos of lines 39C-X and HS-2 were treated with MNase (concentrations 0, 0.04, 0.08, 0.12, and 0.24 U/μl). The purified DNA was cut with SalI, size separated by gel electrophoresis, and transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane, and the membrane was hybridized with a 93-bp fragment from the barley cDNA to map the hsp26-pt transgene. The positions of the proximal and distal hypersensitive sites (PDH and DDH, respectively) in the 39C-X samples are indicated. Control digestion of purified DNA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. A map of the hsp26-pt transgene, indicating the position of the probe, is shown below the gel. (B) A scan of the MNase (0.12 U/μl) digest samples, showing the shift in pattern at the 5′ regulatory region of the gene. Accessible sites in 39C-X (black circles) and HS-2 (white circles) are indicated. (C) DNA samples from a MNase digest done as described above were cut with SacI and SacII, and the DNA samples were size separated by gel electrophoresis, transferred to a nylon filter, and hybridized with the pt DNA fragment to map the hsp70-white transgene. The parental DNA fragment (Prt) and the 5′ DH sites are indicated. The SacI and SacII restriction sites in the P element are shown on the map below.