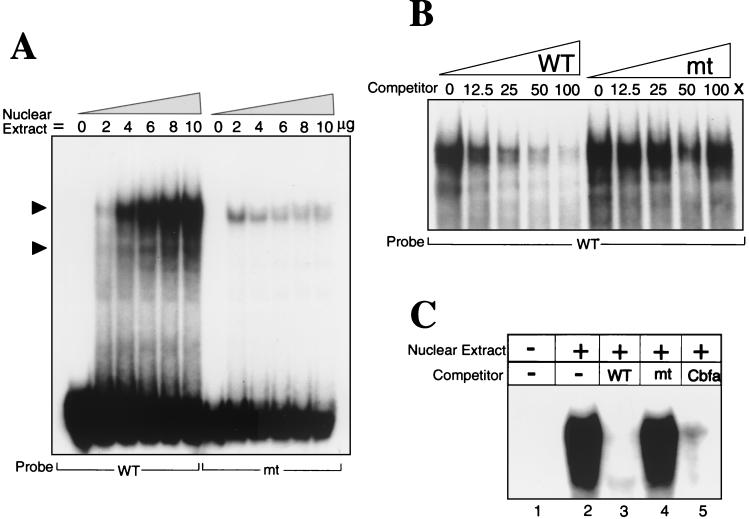
FIG. 4.
Sequence-specific protein-DNA interactions at the proximal Cbfa site 2 in the Gallus BSP promoter. (A) Oligonucleotides representing wild type (WT) and mutant (mt) sequences for each Cbfa site (Fig. 1) were incubated with increasing concentrations (0 to 10 μg) of nuclear extracts from ROS 17/2.8 cells and examined by gel mobility shift assay Solid arrowheads indicate the formation of different specific complexes. Cbfa-related proteins bind with sequence specificity to all four proximal BSP Cbfa motifs, but representative data are shown only for site 2. The results of competition studies shown in panels B and C demonstrate sequence-specific protein-DNA binding complexes at the BSP Cbfa sites. (B) WT probe was incubated with 6 μg of ROS 17/2.8 nuclear extracts and increasing concentrations (0, 12.5, 25, 50, and 100×) of either WT or mutant (mt) oligonucleotides. (C) Lane 1, WT labeled probe without nuclear extract; lane 2, probe with 6 μg of ROS 17/2.8 nuclear extract; lanes 3, 4, and 5, competition with 100X unlabeled wild-type, mutant, and Cbfa consensus sequence oligonucleotides (Fig. 1), respectively. Only the portion of the gel containing the complexes is shown.