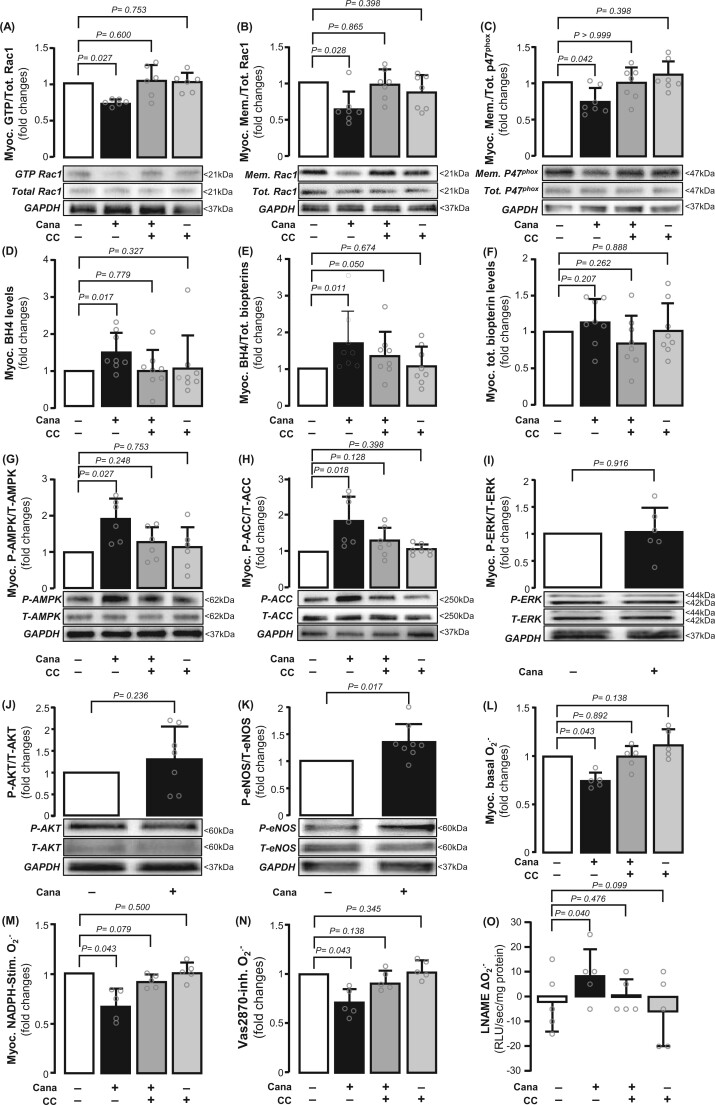
Figure 3.
Effects of canagliflozin on myocardial NADPH oxidase activity and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) coupling status in the human atrial myocardium. Canagliflozin (10 μM for 1 h) inhibited GTP activation (A) and membrane translocation (B) of Rac1, as well as the membrane translocation of p47phox (C). Canagliflozin increased myocardial BH4 but not total biopterin content (D–F). Canagliflozin induced AMPK Thr172 phosphorylation (G) and downstream acetyl-coA carboxylase (ACC) Ser79 phosphorylation (H). These were prevented by the AMPK inhibitor, compound C (CC) (G and H). Canagliflozin did not affect ERK or AKT phosphorylation (I and J). Canagliflozin induced NOS Ser1177 phosphorylation (K). Compound C prevented the effects of canagliflozin on Rac1 activation, BH4 bioavailability (A-F), generation (L–N), and NOS coupling (O). n = 5–8 pairs in panels A–O. Data are presented as mean ± SD. P-values are calculated by Wilcoxon signed-rank test (A–N) and paired t-test (O).